-
Research Paper
- Selective Evaluation of Anticancer and Antibacterial Activities using Piper Longum’s Fruit Derived Silver Nanoparticles Against HeLa Cancer Cell Line
- Sankar Kumar Meenakshisundaram, Sailatha Ethirajulu, and Gunasekaran Sethu
- The methanolic fruit extract of Piper longum and a silver nitrate solution were used to produce silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs). The phytochemicals present …
- The methanolic fruit extract of Piper longum and a silver nitrate solution were used to produce silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs). The phytochemicals present in the extract served as stabilising and reducing agents in this environmentally benign method, allowing stable nanoparticles to develop without the need for harsh chemicals. The obtained nanoparticles were subjected to a series of characterization techniques to confirm their formation and properties. Through optical absorption tests, UV-Visible spectroscopy revealed the surface plasmon resonance band, validating nanoparticle synthesis. Powder X-ray diffraction (P-XRD) revealed information about their crystalline structure. Energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDAX) was used to confirm the elemental composition, while scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to analyse shape and surface characteristics. In addition to structural characterisation, the biological potential of the produced Ag-NPs was investigated. To assess their effectiveness at preventing bacterial growth, antibacterial investigations were carried out against strains of Enterococcus faecalis, Pseudomonas sp., Klebsiella sp., and Vibrio sp. The synthesized nanoparticles exhibited significant cytotoxicity against HeLa cell lines, with an IC50 value of 62.5 µg/mL, corresponding to 54.32 % inhibition. These findings suggest that Piper longum-derived Ag-NPs possess strong anticancer potential against the HeLa (Henrietta Lacks) cell line. - COLLAPSE

-
Research Paper
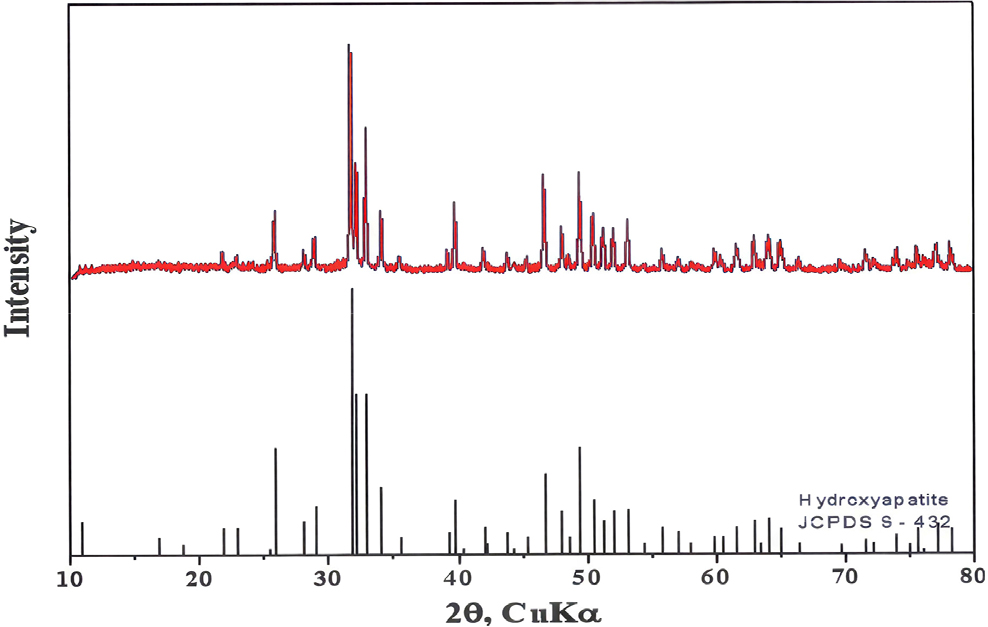
- Effect of the Ultraviolet Protection according to the Concentration of Hydroxyapatite
- Su-Chak Ryu, Jae-Hun Jeong, Dong-Hun Lee
- Sunblocks are materials used in creams to help limit exposure to UVA and UVB. Many sunscreens contain TiO2 and ZnO as …
- Sunblocks are materials used in creams to help limit exposure to UVA and UVB. Many sunscreens contain TiO2 and ZnO as the primary sunblock materials. In this study, we manufactured a sunscreen lotion using hydroxyapatite (HAp) nano-sol instead of ZnO and TiO2. HAp is a biomaterial widely used in applications such as bone grafting, so it is known to be very biocompatible. In the present work, HAp-water nano sol, ZnO-water nano sol, and TiO2-water nano sol were prepared by the attrition milling method. The sunscreen lotion base (LB) was manufactured with some oil and water. Lotions with various HAp-water solutions and LB concentrations were fabricated and their UV absorbance was measured. 6 % HAp content was the optimal amount considering price. The sun protection factor (SPF) value at that level was approximately 20 on average, corresponding to about 95 % UV protection. Results confirmed that ultraviolet screening agents using HAp had an excellent ultraviolet blocking effect. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Paper
- Fluorescent Tunability of Waterborne Polyurethane Modified by Schiff Base Cu(II) Complexes
- Xin Bu, Tianfu Wang, Kaixuan Shao, Kehua Zhang, Mingdi Yang, Xianhai Hu
- In the field of high-end optics, the demand for fluorescent-tunable polymers is increasingly urgent. However, traditional fluorescent materials have limitations including insufficient …
- In the field of high-end optics, the demand for fluorescent-tunable polymers is increasingly urgent. However, traditional fluorescent materials have limitations including insufficient stability, poor processability, and volatile organic compound (VOC) pollution. In this study, using an improved acetone method synthesis process, Schiff base Cu(II) complexes were innovatively introduced into the main chain of waterborne polyurethane (WPU), to successfully prepare fluorescence-controllable PMBxCu1-WPU (x = 1, 2, 3), realizing the stable bonding of the Schiff base ligand (PMB) and Cu(II) in the polyurethane chain. The successful synthesis of PMB and the structure of the PMBxCu1-WPU were confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray powder diffractometer and other testing methods. It was found that the particle size of PMBxCu1-WPU increased by increasing Cu(II) content, and the absolute value of its Zeta potential exceeded 40 mV, showing excellent dispersion stability. PMBxCu1-WPU still maintained good thermal stability, with an initial decomposition temperature of about 220 °C. With the increase in Cu(II) coordination degree, the UV-vis absorption peak undergoes a certain degree of redshift. It is worth noting that after PMB was incorporated into WPU, its emission peak redshifted from 499 nm to 551 nm; with the increase of Cu(II) coordination degree, the emission peak further blue-shifted to 534 nm, which indicates that the fluorescence emission wavelength of PMBxCu1-WPU can be precisely regulated by the coordination degree of Cu(II). This study provides a new method for developing high-performance fluorescent-tunable waterborne polyurethane, and has potential application in the fields of intelligent anti-counterfeiting and biomedicine. - COLLAPSE

-
Research Paper
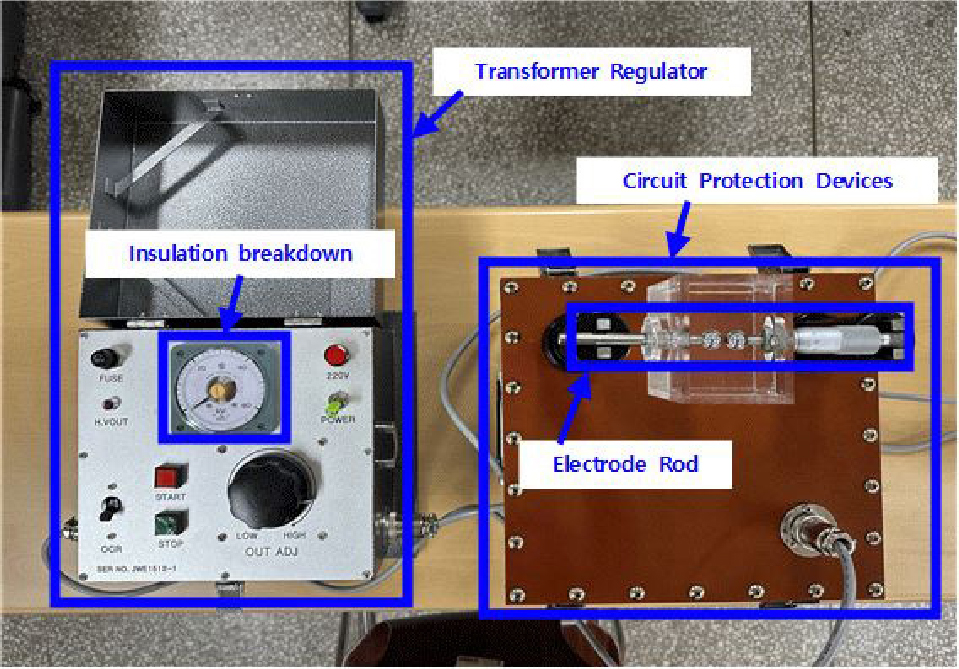
- Electrical Properties of Liquid Insulation Oil under Varying Electrode Shapes and Temperatures
- Tae-Hee Kim, Seo Yeon An, Geun Ho Gim
- In this paper, considering the temperature characteristics relevant to the climatic conditions of our country, an experimental study was conducted to investigate …
- In this paper, considering the temperature characteristics relevant to the climatic conditions of our country, an experimental study was conducted to investigate whether the electrical characteristics of transformer insulating oil vary with changes in electrode configuration and temperature. To achieve this objective, three representative electrode types—the sphere electrode, the plate electrode, and the needle electrode—were selected to simulate the different electric field distributions commonly encountered in transformer systems. Based on these electrode types, six electrode combinations were examined: sphere-sphere, plate-plate, sphere-plate, needle-needle, sphere-needle, and needle-plate configurations. To evaluate the influence of gap spacing on insulation performance for each electrode combination, the distance between electrodes was systematically adjusted in four incremental steps of 1.5, 2.0, 2.5 and 3.0 mm. Furthermore, the ambient temperature of the insulating oil was varied at four levels 0, 10, 20 and 30 °C, to reflect typical operating and environmental conditions. The electrical properties under these conditions were analyzed to determine the combined effects of electrode geometry and temperature variation on the insulating characteristics of transformer insulating oil. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Paper
-
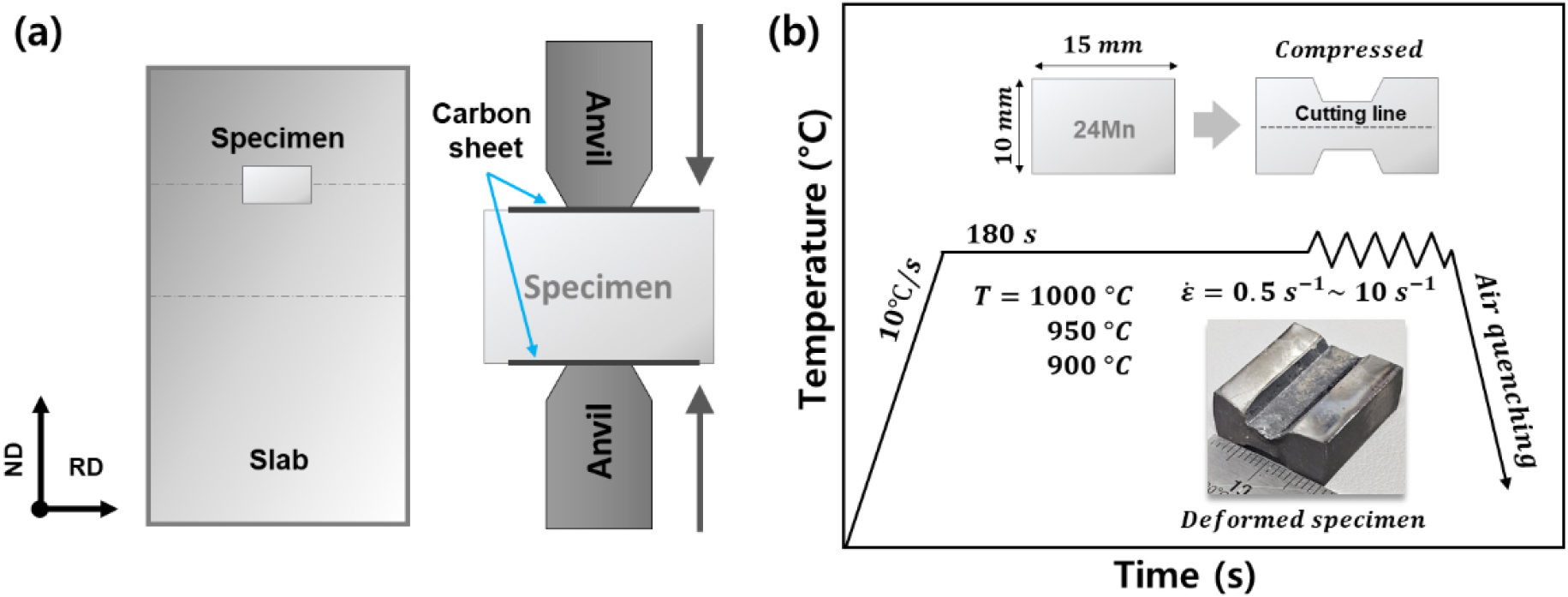
Hot Deformation Behavior and Dynamic Recrystallization Characteristics of an Fe-24Mn Slab during Plane-Strain Compression
평면 변형 압축 시험을 이용한 Fe-24Mn 슬래브의 고온 변형 거동 및 동적 재결정 특성
-
Changwoo Lee, Byoungkoo Kim, Jae Jun Lee
이창우, 김병구, 이재준
- This study investigated the hot deformation behavior and dynamic recrystallization (DRX) characteristics of a coarse-grained Fe-24Mn steel slab using plane strain compression …
- This study investigated the hot deformation behavior and dynamic recrystallization (DRX) characteristics of a coarse-grained Fe-24Mn steel slab using plane strain compression (PSC) tests. Tests were conducted at 900-1,000 °C and strain rates of 0.5-10 s-1. Constitutive equations based on the Zener-Hollomon parameter accurately predicted flow stress (R=0.945). A processing map based on the Dynamic Materials Model (DMM) predicted flow instability at high strain rates (10 s-1) due to a negative strain rate sensitivity exponent. However, electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) analysis revealed that these regions actually exhibited a fully recrystallized microstructure with low Kernel Average Misorientation (KAM) values, contradicting the DMM prediction. This discrepancy is attributed to adiabatic heating during high-speed deformation, which induces thermal softening and provides the driving force for DRX. Consequently, the region with negative power dissipation efficiency at high strain rates should be reinterpreted not as a failure zone, but as a window for efficient microstructural refinement. The study identifies 950 °C and 10 s-1 as the optimal processing conditions for grain refinement of the as-cast slab. - COLLAPSE
-
Hot Deformation Behavior and Dynamic Recrystallization Characteristics of an Fe-24Mn Slab during Plane-Strain Compression
Journal Informaiton
 Korean Journal of Materials Research
Korean Journal of Materials Research
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Korean Journal of Materials Research
Korean Journal of Materials Research











