-
Research Paper
-
Hot Deformation Behavior of PH13-8Mo Stainless Steel
PH13-8Mo 스테인리스강의 고온 변형 거동
-
Changwoo Lee, Byoungkoo Kim, Jae Jun Lee
이창우, 김병구, 이재준
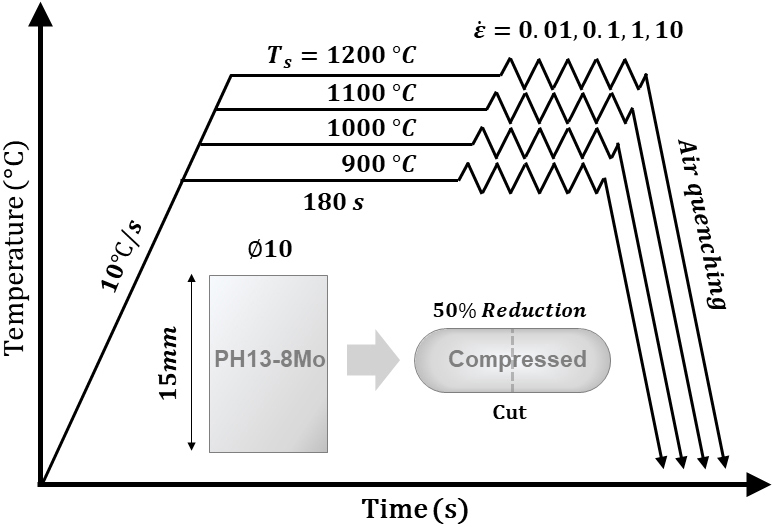
- This study investigated the hot deformation behavior and microstructural evolution of PH13-8Mo precipitation-hardening stainless steel. Hot compression tests were performed at temperatures …
- This study investigated the hot deformation behavior and microstructural evolution of PH13-8Mo precipitation-hardening stainless steel. Hot compression tests were performed at temperatures ranging from 900 to 1,200 °C and strain rates of 0.01 to 10 s-1. Constitutive equations based on the Zener-Hollomon parameter were established by considering the compensation of strain, where the material constants were fitted with 6th-order polynomials. The established model showed high predictability with a correlation coefficient of 0.994 and an average absolute relative error of 4.39 %. A hot processing map was developed based on the Dynamic Materials Model, identifying unstable regions characterized by negative instability criteria under low-temperature/high-strain-rate conditions, as well as specific moderate-rate zones. Electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) integrated analysis [inverse pole figure (IPF), kernel average misorientation (KAM), and grain orientation spread (GOS)] revealed that while dynamic recrystallization promoted grain refinement through necklace structures at 900 °C and 0.01 s-1, high-temperature deformation at 1,200 °C led to significant grain coarsening and high transformation-induced stress. Furthermore, regions of instability were confirmed to cause flow localization and strain hotspots, detrimental to structural integrity. Consequently, the moderate temperature region around 1,100 °C with a low strain rate is proposed as the optimal window for achieving uniform and stable prior austenite grain structures. - COLLAPSE
-
Hot Deformation Behavior of PH13-8Mo Stainless Steel
-
Research Paper
-
Design of High-Entropy Alloys Using Conditional Generative Models and Multi-objective Bayesian Optimization
조건부 생성 모델과 다중 목적 베이지안 최적화를 활용한 고엔트로피 합금 설계
-
Mingyu Kim, Chunghee Nam
김민규, 남충희
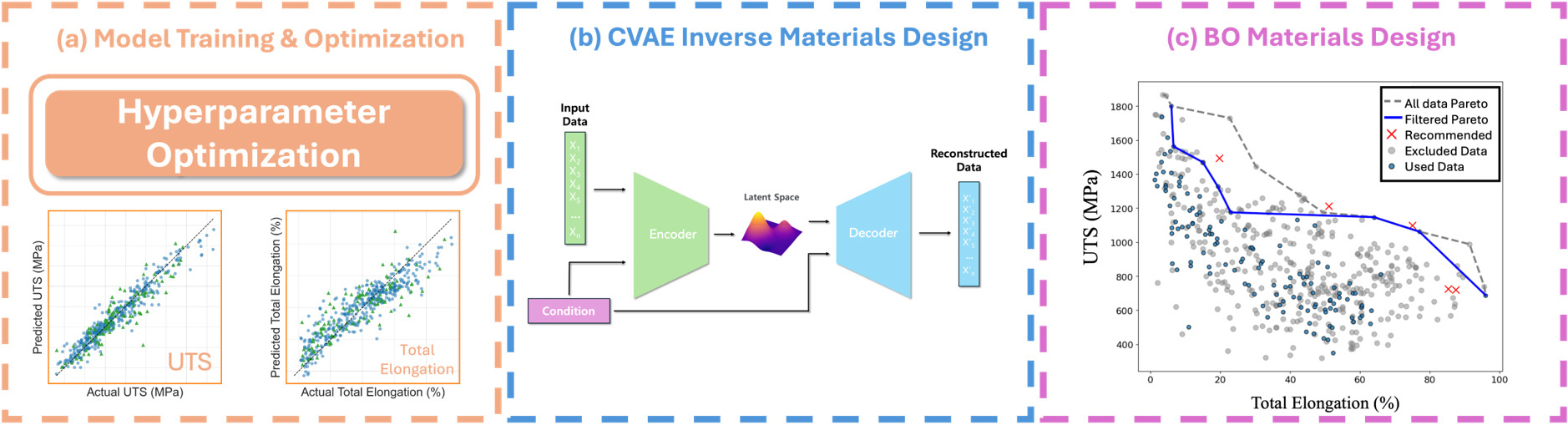
- This study of a high-entropy alloy (HEA) explored two strategies to simultaneously satisfy two mechanical properties, ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and total …
- This study of a high-entropy alloy (HEA) explored two strategies to simultaneously satisfy two mechanical properties, ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and total elongation. The first strategy used inverse design based on a conditional variational autoencoder (CVAE), and the second employed multi-objective Bayesian optimization. Using a dataset of 501 literature-based HEAs, three models were trained with alloy composition and experimental conditions as inputs. Among these, extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) exhibited the highest predictive performance for both properties and was selected as the final prediction model. CVAE was employed to generate 1,000 new samples from the latent space under the condition that both UTS and total elongation exceeded their mean values. Of these, 310 physically feasible compositions were validated using the XGBoost model, and approximately 17.7 % satisfied the target properties. Next, expected hypervolume improvement (EHVI)-based Bayesian optimization, beginning with 130 initial compositions that demonstrated superior properties, proposed five recommended candidates. These samples were found to differ in compositional characteristics from the existing dataset, which can be interpreted as exploration driven by the uncertainty of the probabilistic machine learning model. The candidate compositions generated by both methods were predicted by the XGBoost model to have the potential to achieve the target properties. - COLLAPSE
-
Design of High-Entropy Alloys Using Conditional Generative Models and Multi-objective Bayesian Optimization
-
Research Paper

-
Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Performance of Vertical MoS2 through Controllable Chemical Vapor Deposition
제어 가능한 화학기상증착법을 통한 수직 MoS2의 향상된 광전기화학 성능
-
Dong-Bum Seo, Eui-Tae Kim
서동범, 김의태
- One way to increase the adoption of renewable energy technologies is to develop advanced materials that improve the efficiency of photoelectrochemical (PEC) …
- One way to increase the adoption of renewable energy technologies is to develop advanced materials that improve the efficiency of photoelectrochemical (PEC) systems. As a two-dimensional semiconductor, MoS2 exhibits strong absorption in the visible light region and high catalytic activity, making it a promising photoelectrode material for PEC applications. Nevertheless, systematic studies aimed at optimizing its properties remain necessary. In this study, the morphology of MoS2 photoelectrodes for PEC applications was controllably engineered by adjusting the deposition time using a metal-organic chemical vapor deposition process. The PEC photocurrent of vertically grown MoS2 nanosheet structures was markedly higher than that of MoS2 nanoparticles. This enhancement is attributed to (i) efficient charge separation within the nanosheet architecture, (ii) improved light absorption, and (iii) an increase in the density of catalytically active sites. In addition, the photocurrent depends on the nanosheet size, with excessively thick nanosheets exhibiting lower performance due to limited photogenerated carrier diffusion lengths. These results provide a systematic photoelectrode design strategy with an optimized morphology for efficient PEC water splitting. - COLLAPSE
-
Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Performance of Vertical MoS2 through Controllable Chemical Vapor Deposition
-
Research Paper
-
Improved Electrical Performance of Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor High-Electron-Mobility Transistors (MOS-HEMTs) Using Al2O3/HfO2 Stacked Gate Dielectrics
Al2O3/HfO2 스택 구조의 게이트 산화막을 이용한 Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor High-Electron-Mobility Transistors (MOS-HEMTs) 전기적 특성 향상
-
Seokhyun Han, Jihoon Lee, Hyeonwoo Hwang, Jinsung Park, Bohyeon Kim, Junmo Yang, Younghun Han, Juneo Song, Yoon Seok Kim
한석현, 이지훈, 황현우, 박진성, 김보현, 양준모, 한영훈, 송준오, 김윤석
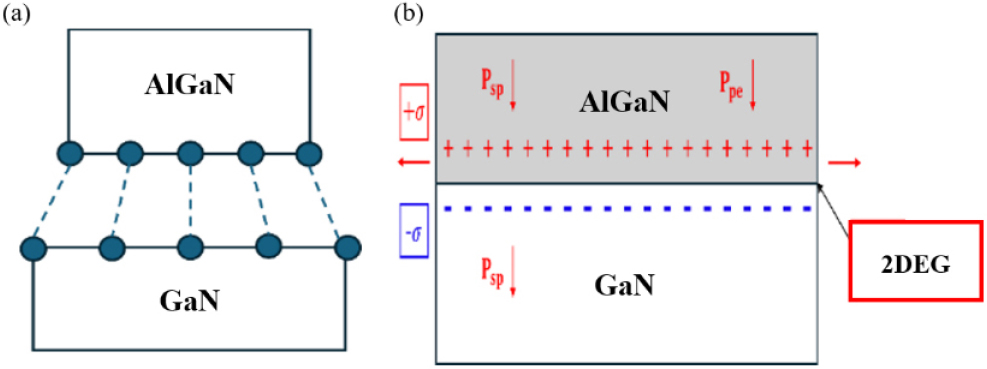
- AlGaN/GaN high-electron-mobility transistors (HEMTs) are widely employed in power electronics and high-frequency systems because of their high-speed switching and high-power capabilities. However, …
- AlGaN/GaN high-electron-mobility transistors (HEMTs) are widely employed in power electronics and high-frequency systems because of their high-speed switching and high-power capabilities. However, conventional structures suffer from issues including mobility degradation and device deterioration at elevated temperatures, as well as current collapse and increased gate leakage under high-voltage operation. To address these issues, this work proposes metal-oxide-semiconductor HEMTs (MOS-HEMTs) incorporating an Al2O3/HfO2 stacked gate dielectric. Al2O3 provides excellent chemical stability at the AlGaN interface, reducing interface trap density, while its wide bandgap suppresses electron tunneling and lowers gate leakage. In contrast, HfO2 offers a high dielectric constant, improving oxide capacitance and enhancing charge control even at the same physical thickness. The stacked Al2O3/HfO2 structure leverages the complementary advantages of both materials, enabling threshold voltage stabilization and effective suppression of leakage current. This design mitigates the thermal and electrical reliability concerns of conventional HEMTs and paves the way for high-performance GaN-based devices suited to next-generation high-speed, high-power applications such as artificial intelligence, 5G communication, and LiDAR systems. - COLLAPSE
-
Improved Electrical Performance of Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor High-Electron-Mobility Transistors (MOS-HEMTs) Using Al2O3/HfO2 Stacked Gate Dielectrics
Journal Informaiton
 Korean Journal of Materials Research
Korean Journal of Materials Research
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Korean Journal of Materials Research
Korean Journal of Materials Research











