-
Review
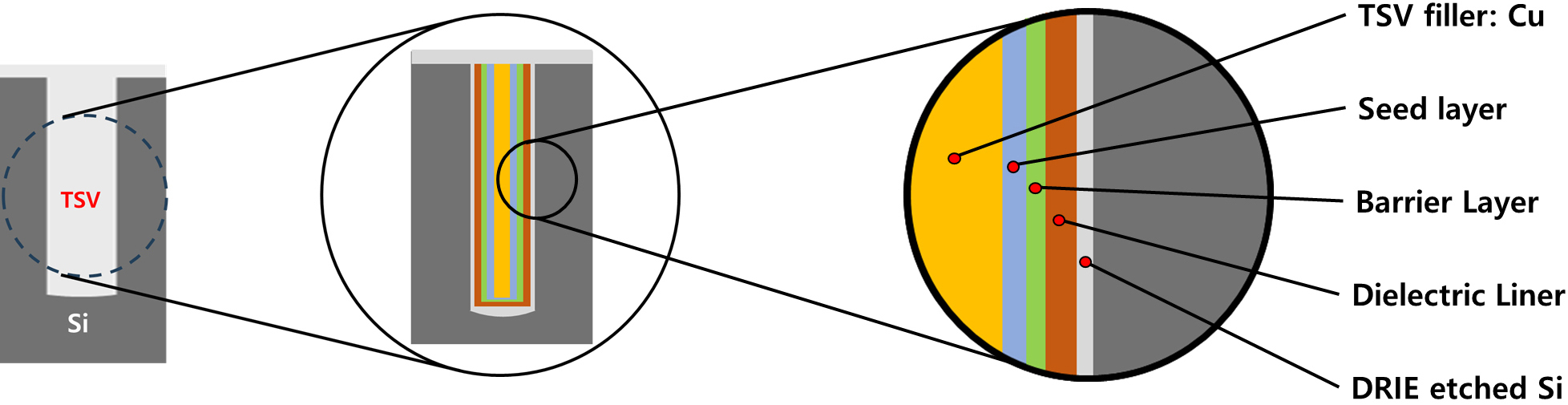
-
Cu Filling into Seed and Seedless Layered Through-Silicon-Via and Hybrid Bonding for High-Density Semiconductor Packaging
고집적 반도체 패키징을 위한 Seed 및 Seedless층 TSV의 Cu 충전 및 하이브리드 본딩
-
Chae Yeon Lim, Shin Hui Seon, Hyun-Sik Kim, Jae Pil Jung
임채연, 선신희, 김현식, 정재필
-
Cu Filling into Seed and Seedless Layered Through-Silicon-Via and Hybrid Bonding for High-Density Semiconductor Packaging
-
Research Paper
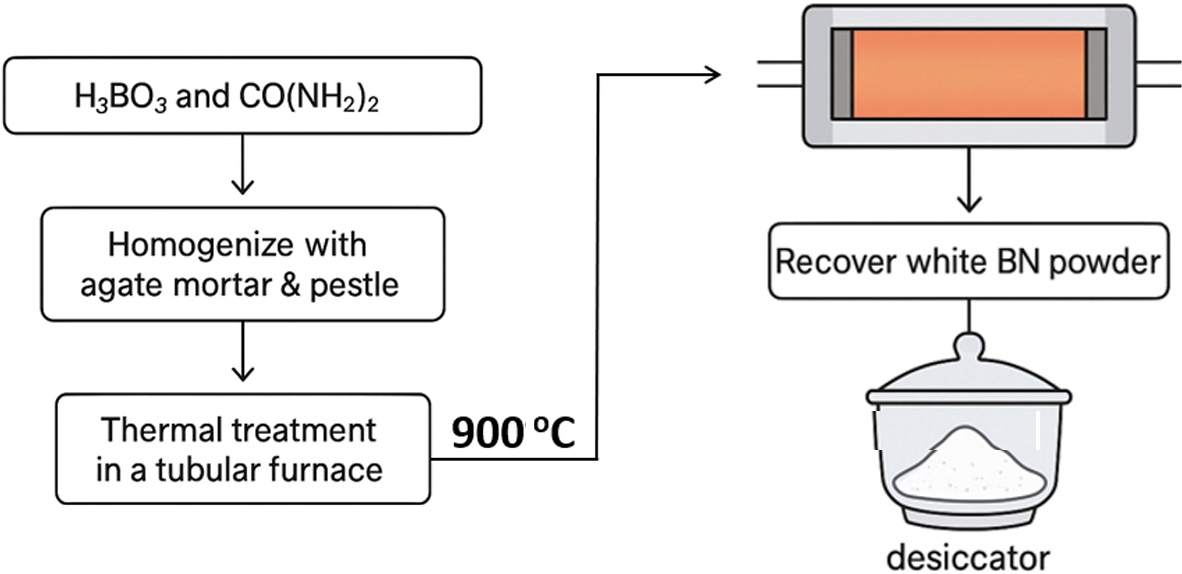
- Layered and Polycrystalline Architectures of Boron Nitride Unveiled by Electron Microscopy
- Ankita Yadav, Mukesh Kumar, Ashutosh Sharma
-
Research Paper
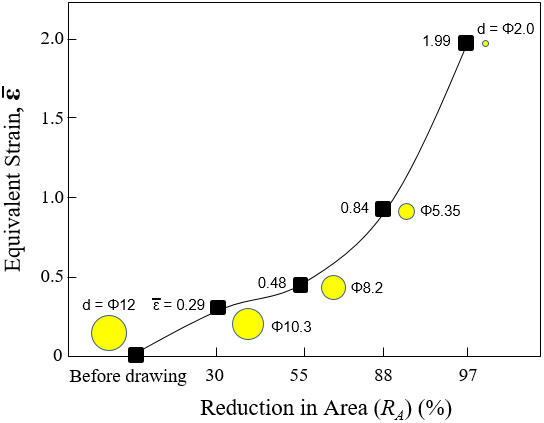
-
Changes in Microstructure, Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Al-Fe-Mg-Cu-B System Aluminum Alloy Wire with Cold Drawing Process
인발공정에 따른 Al-Fe-Mg-Cu-B계 알루미늄합금 선재의 미세조직, 기계적 및 전기적 특성 변화
-
Hyeon-Jun Heo, Handong Cho, Seong-Hee Lee
허현준, 조한동, 이성희
-
Changes in Microstructure, Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Al-Fe-Mg-Cu-B System Aluminum Alloy Wire with Cold Drawing Process
-
Research Paper
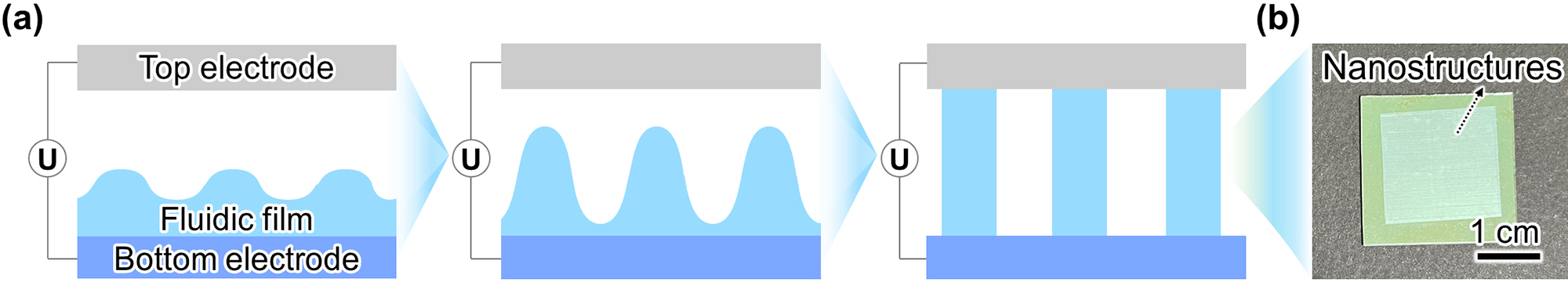
-
Research Paper
-
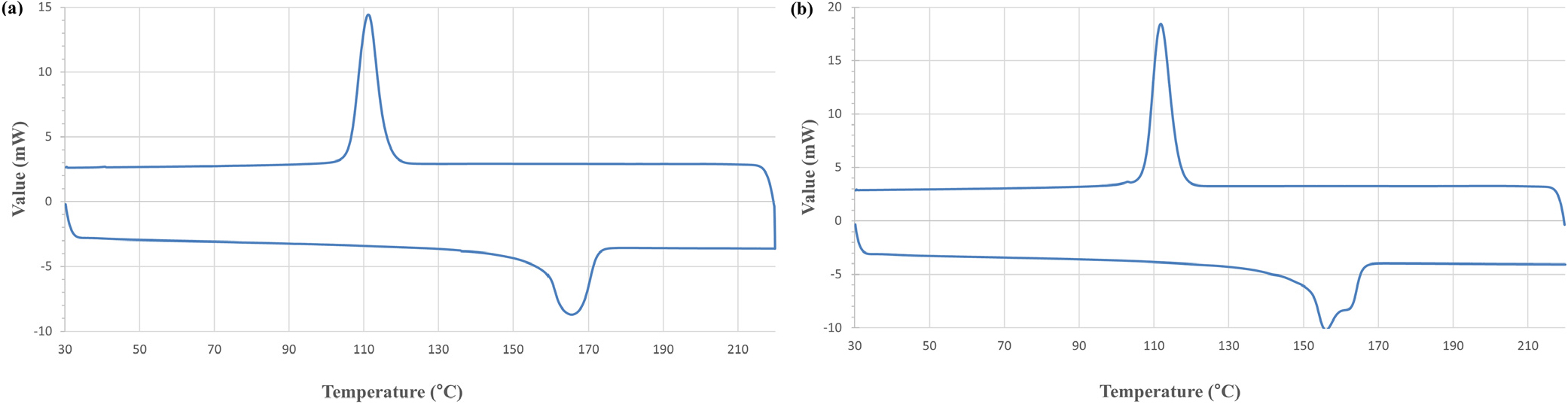
Changes in the Physical Properties of Polypropylene Resin by E-beam Irradiation
전자선 조사에 의한 폴리프로필렌 수지의 물리적 특성 변화
-
Junghoo Lee, Yongseok Cho
이정후, 조용석
-
Changes in the Physical Properties of Polypropylene Resin by E-beam Irradiation
-
Research Paper
-
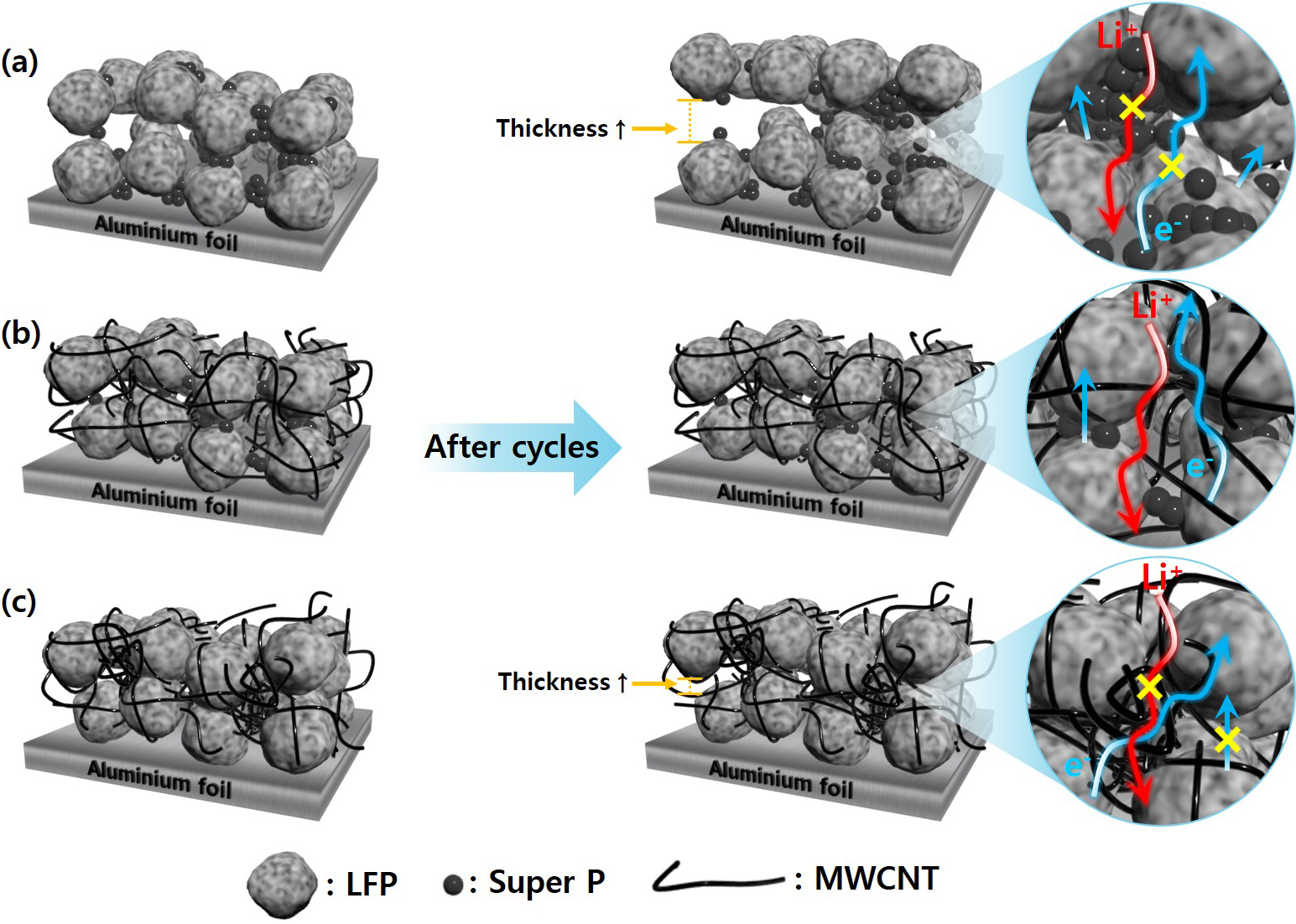
Design of Conductive Network through the Hybrid Application of Super P and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube in Thick LiFePO4 Electrodes
LFP 후막전극에 Super P와 MWCNT의 복합 적용을 통한 전도성 네트워크 설계
-
Hyeong-Rae Kim, Myeong-Hun Jo, Hyo-Jin Ahn
김형래, 조명훈, 안효진
-
Design of Conductive Network through the Hybrid Application of Super P and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube in Thick LiFePO4 Electrodes
Journal Informaiton
 Korean Journal of Materials Research
Korean Journal of Materials Research
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Korean Journal of Materials Research
Korean Journal of Materials Research











