-
Review
-
Current Status of Zinc Oxide Nanopowder Manufacturing Technology for UV Filters
자외선 차단제용 ZnO 나노 분말 제조기술 현황
-
Hyun Seon Hong
홍현선
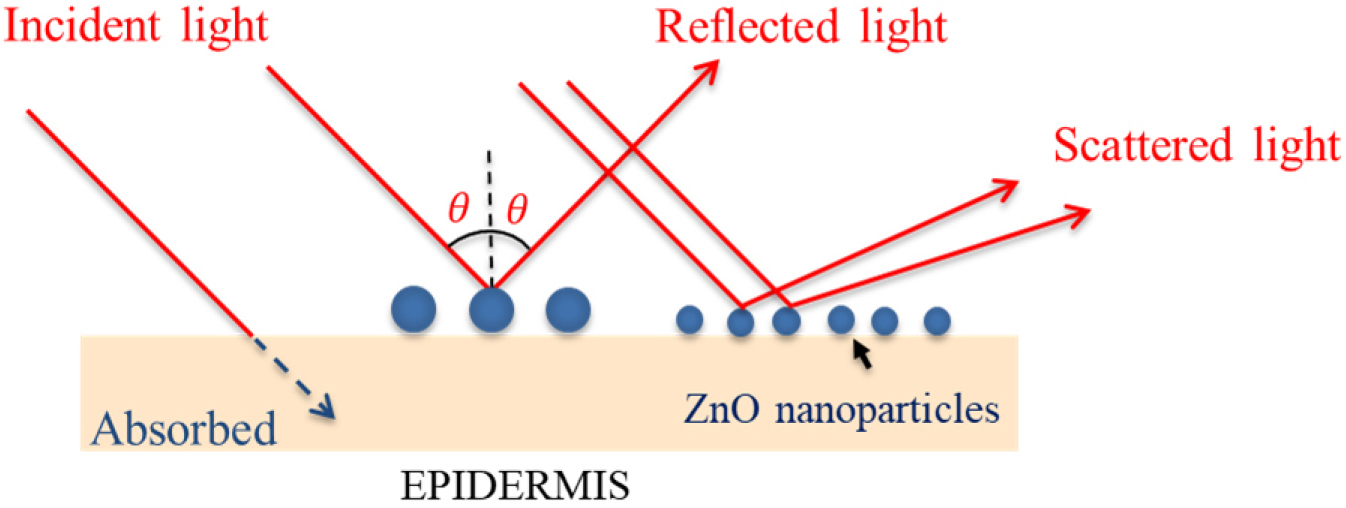
- Zinc oxide has attracted attention due to its high functionality, including chemical stability, high biocompatibility, and excellent optical properties. In particular, when …
- Zinc oxide has attracted attention due to its high functionality, including chemical stability, high biocompatibility, and excellent optical properties. In particular, when the particles are nano-sized, they exhibit new characteristics, making them suitable for application in UV-filters, photo-catalysts and cosmetics. This paper provides an overview of nano zinc oxide used for UV filters, and summarizes domestic and international production technology and the industrial status of zinc oxide nano-powder. First, the concept and principle of the nano-sized zinc oxide manufacturing process is provided, and various types of manufacturing methods are analyzed, namely, wet process, dry process, and powder process. Next, the results of an analysis of the domestic sunscreen market size and company status are provided. The production processes of major domestic companies and their product characteristics, such as particle size, purity, surface treatment, and transparency of the zinc oxide powder being produced, are analyzed and provided. The characteristics of zinc oxide produced for use in sunscreens, both domestically and internationally, can be summarized as follows. Manufactured zinc oxide powder is white or transparent, and particle size typically ranges from 30 to 200 nm on average, although non-nano sized powders have also been developed in recent years. When used as a coating, the surface to be coated is typically treated with substances such as silicone oil or silane, and the powder is formulated into products by dispersing it in oil- or water-based systems. - COLLAPSE
-
Current Status of Zinc Oxide Nanopowder Manufacturing Technology for UV Filters
-
Research Paper
- Elucidating the Role of Nb2O5 and Sb2O3 Coating on the Electrochemical Performance of Co-free Li- and Mn-rich Layered Oxide Cathode
- Beomsoo Kim, Taehun Jeon, Chunjoong Kim
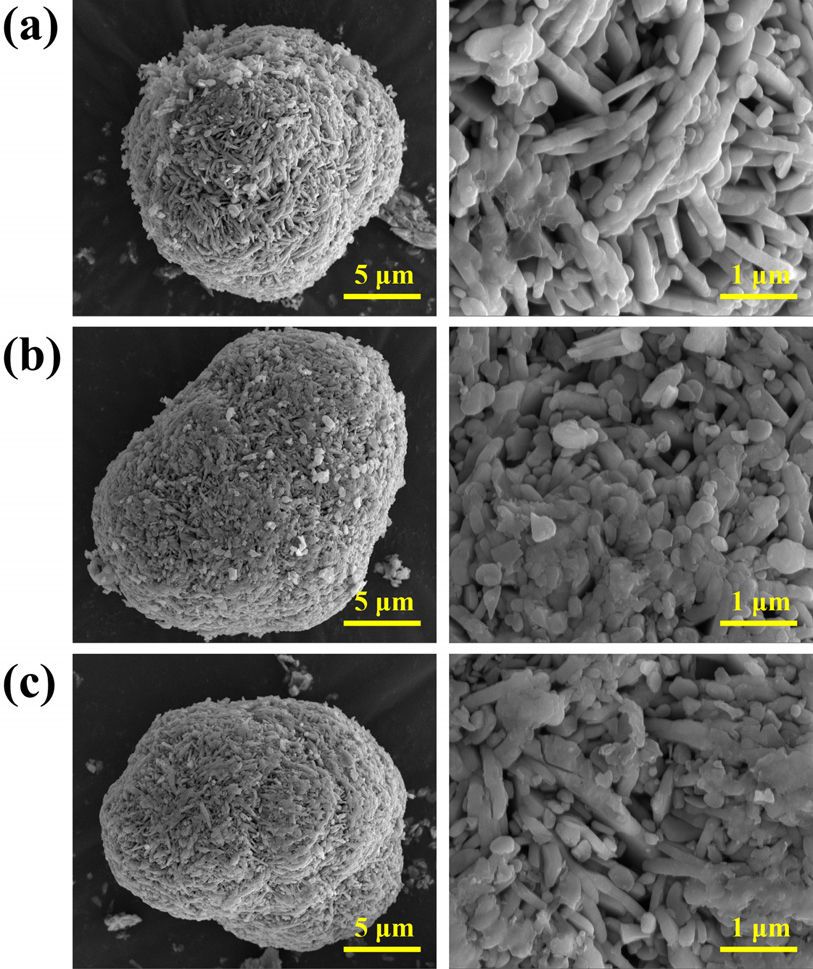
- Lithium- and manganese-rich layered oxide (LMRO) is considered a promising cathode material for lithium-ion batteries owing to its high capacity and energy …
- Lithium- and manganese-rich layered oxide (LMRO) is considered a promising cathode material for lithium-ion batteries owing to its high capacity and energy density. However, operation at a high voltage of 4.8 V leads to several issues including low Coulombic efficiency, poor cycle life, slow kinetics, and voltage decay due to spinel phase transition, hindering commercialization. Herein, we synthesized a cobalt-free LMRO cathode and studied the effect of Nb2O5 and Sb2O3 coating layers on electrochemical performance. The Nb2O5 coating facilitated the formation of a LiNbO3 layer, which enhanced the initial electrochemical performance, including Coulombic efficiency and energy density. Meanwhile, Sb2O3 not only coated the surface but also doped into the bulk structure, thereby increasing capacity and improving rate capability. Comparative analysis using materials with different structural solubility revealed how oxide coatings influenced lithium-ion transport and electrochemical behavior. This study highlights the importance of interfacial engineering for optimizing LMRO cathodes for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Paper
-
Main Effects of Additives on Copper Electroplating at High Current Density
고전류밀도 구리전해도금에서 첨가제의 주요효과
-
Tae-Gyu Woo, Il-Song Park
우태규, 박일송
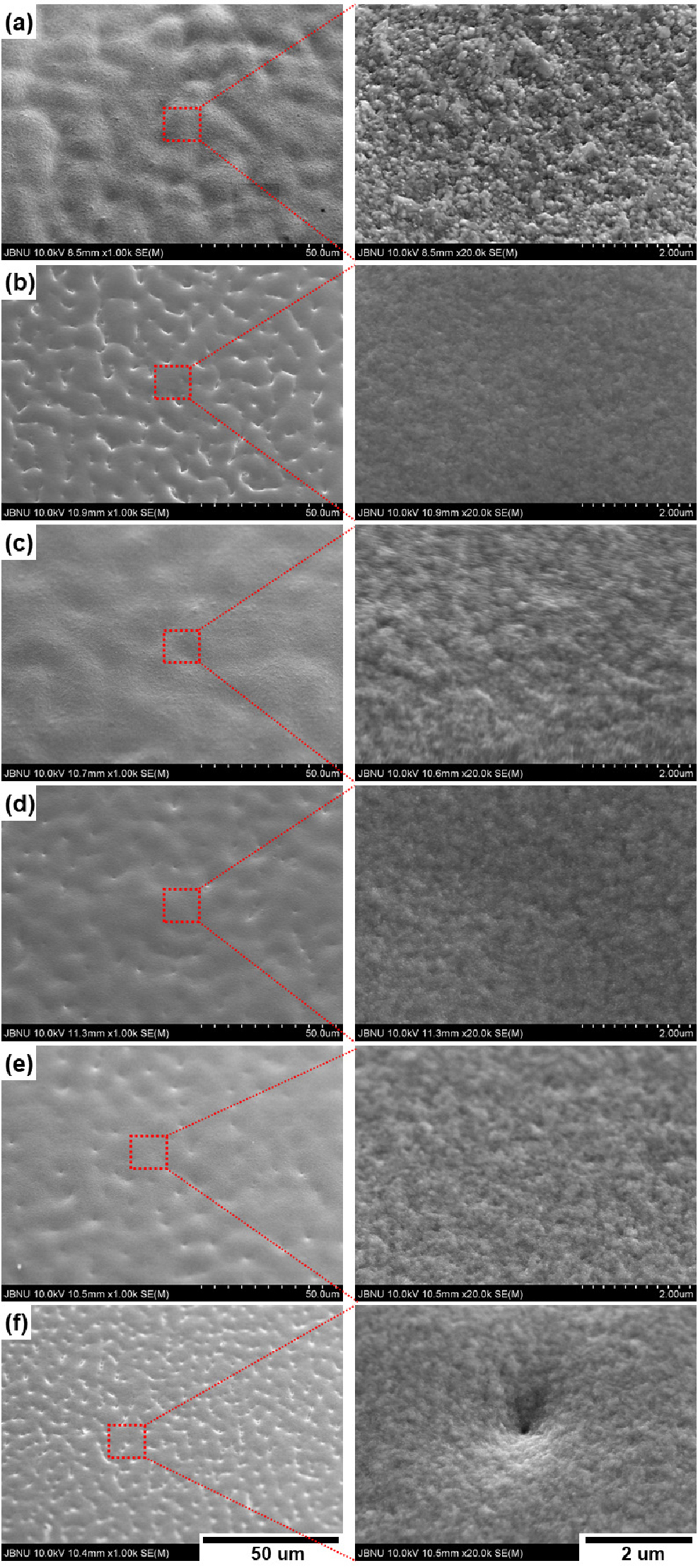
- This study investigates the changes in the surface characteristic, electrical and mechanical properties of copper foils electrodeposited in electrolytes with added various …
- This study investigates the changes in the surface characteristic, electrical and mechanical properties of copper foils electrodeposited in electrolytes with added various additives (Janus Green B (JGB), 3–mercapto–1–propane sulfonic acid (MPSA), Polyethylene glycol (PEG) and Chloride ion) under high current density. The main effect of additives on these properties was analyzed. In the group with added JGB, the crystal size on the surface became finer, and a homogeneous surface was observed. However, dented areas were observed, which decreased with an increase in chloride ions. When 100 ppm of PEG and 10 ppm of JGB were added, the fine dents on the surface increased. When a certain amount or more of additives were added, defects on the surface occurred due to competition between additives. The addition of JGB induced crystal growth in the direction of the (111) plane. Copper foils with excellent yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation could be obtained with an appropriate crystal size. The addition of JGB mainly affected crystal size and the direction of crystal growth, which is an important factor for controlling mechanical properties. PEG mainly affected elongation, and chloride ions had a primary effect on surface roughness, resistivity, and corrosion rate. Therefore, controlling additives is an effective way to significantly affect the manufacture of copper foil and produce various suitable properties in high demand. - COLLAPSE
-
Main Effects of Additives on Copper Electroplating at High Current Density
-
Research Paper
-
Processing and Reuse of Ready-Mixed Concrete Recovered Water using Nano Nubble CO2 Dissolution Technology
나노버블 CO2 용해 기술을 활용한 레미콘 회수수 처리 및 재이용
-
Jong Kyu Kim
김종규
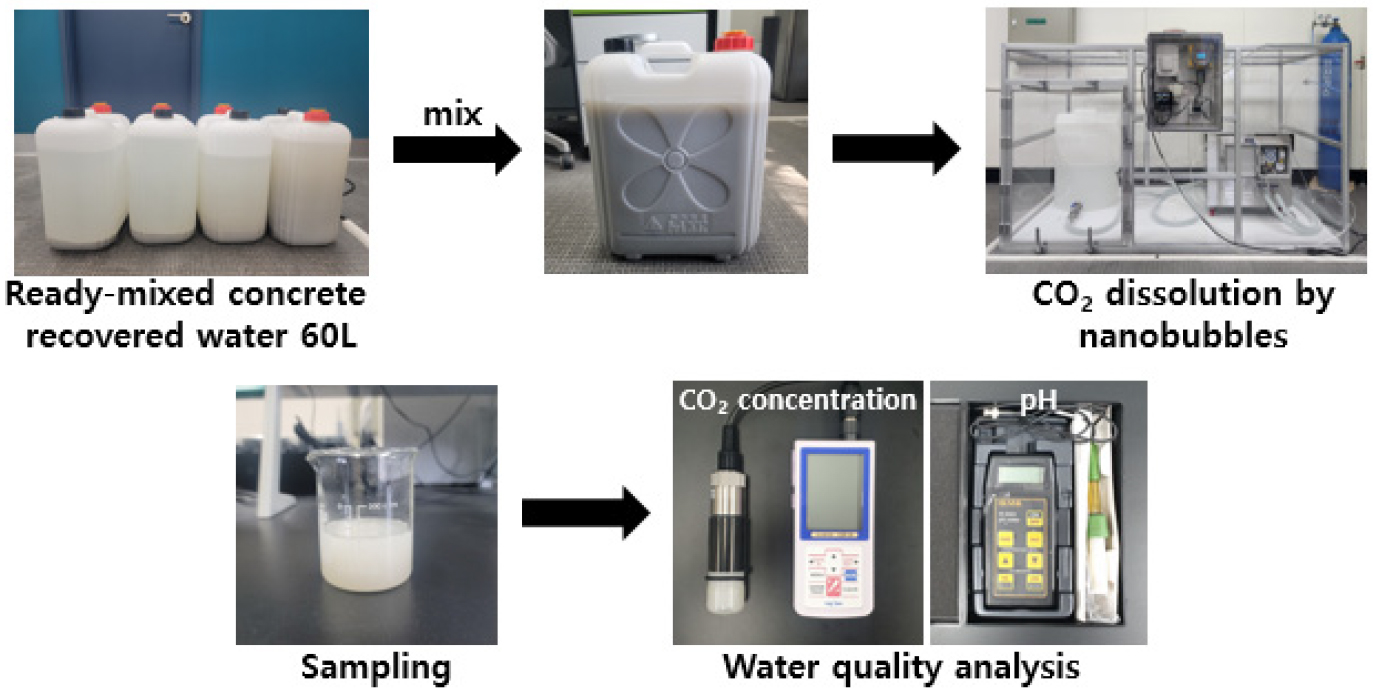
- This research aimed to find an eco-friendly way to neutralize water recovered from ready-mixed concrete by dissolving carbon dioxide in it, and …
- This research aimed to find an eco-friendly way to neutralize water recovered from ready-mixed concrete by dissolving carbon dioxide in it, and to verify the potential use of such water for mixing concrete. Carbon dioxide was injected using nanobubble technology into recovered water, and the optimized conditions for dissolution were established by analyzing the carbon dioxide concentration in the water and measuring pH over time. Mortar was manufactured using this recovered water following carbon dioxide nanobubbles treatment, and measurements of compressive strength and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) were conducted to verify the formation of calcium carbonate. 2,464 mg/L of carbon dioxide was dissolved in the recovered water, and the pH was measured to be 6.34. The compressive strength of the manufactured mortar was found to be 32.02 % stronger than mortar manufactured with normal tap water. According to the thermogravimetric analysis results, the amount of calcium hydroxide produced in the mortar manufactured with recovered water from ready-mixed concrete was 8.10 %, and the production amount of calcium carbonate was 6.49 %. This means that the amount of calcium carbonate produced was greater than that in mortar manufactured with normal tap water, as well as tap water containing nanobubble carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide was stably dissolved in water recovered from ready-mixed concrete using nanobubbles, enabling environmentally friendly neutralization without the use of chemicals. Also, when the recovered water from ready-mixed concrete containing dissolved carbon dioxide was used for mixing concrete, it was determined that the carbonation reaction influenced the formation of calcium carbonate, which contributed to the improvement in concrete strength. - COLLAPSE
-
Processing and Reuse of Ready-Mixed Concrete Recovered Water using Nano Nubble CO2 Dissolution Technology
-
Research Paper
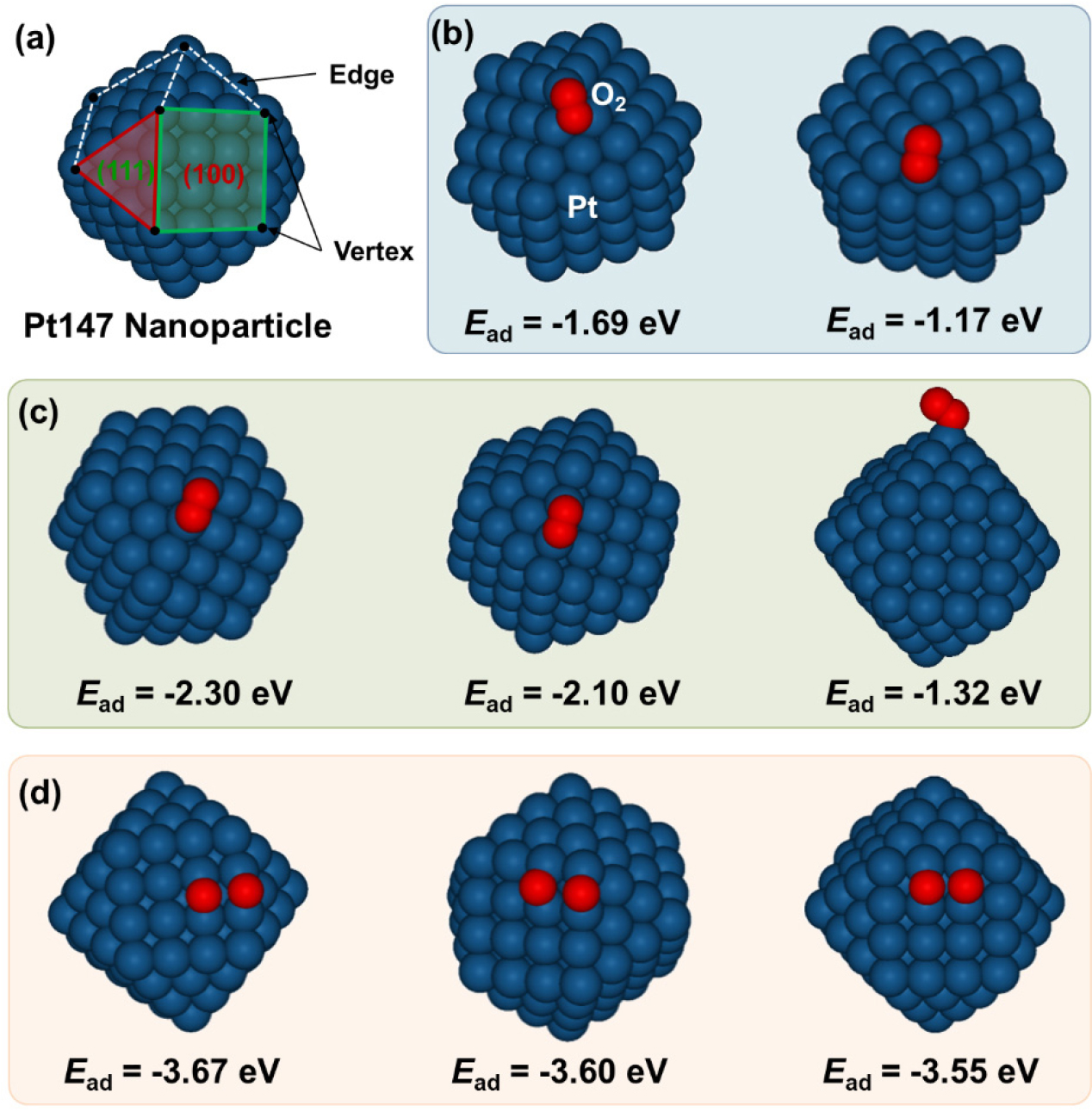
-
Energetic Landscape of Oxygen Activation on Pt147 Nanoparticles
미세면이 형성된 백금 나노입자 표면에서 일어나는 산소의 활성화
-
Ju Hyeok Lee, Jongseok Kim, Yejung Choi, Kihyun Shin, Hyun You Kim
이주혁, 김종석, 최예정, 신기현, 김현유
- We present an atomistic investigation of the oxygen activation of a Pt nanoparticle with 147 atoms (Pt147), focusing on the role of …
- We present an atomistic investigation of the oxygen activation of a Pt nanoparticle with 147 atoms (Pt147), focusing on the role of microfacets. Using density functional theory (DFT) calculations, we evaluated the adsorption energy (Ead) of both molecular and atomic oxygen across the surface, along with the activation energy barrier (Eact) for O2 dissociation and subsequent atomic oxygen diffusion. The Pt147 exhibited a facet-dependent variation in O2 adsorption, while atomic oxygen displayed a relatively uniform Ead across the surface. This suggests that atomic oxygen can readily participate in surface reactions regardless of the location. The diffusion Eact values of atomic oxygen calculated along various pathways were lower than 0.61 eV, confirming the high surface mobility of oxygen atoms. Interestingly, we found a clear linear correlation between the Ead of O2 on Pt147 and the Eact of subsequent O2 dissociation. The results show that Pt nanoparticles with well-developed microfacets can efficiently activate molecular oxygen and facilitate oxidation reactions. - COLLAPSE
-
Energetic Landscape of Oxygen Activation on Pt147 Nanoparticles
Journal Informaiton
 Korean Journal of Materials Research
Korean Journal of Materials Research
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Korean Journal of Materials Research
Korean Journal of Materials Research











