-
Research Paper
- Rheological Behavior of Shear Thickening Fluids with Carbon Nanotube Incorporation
- Young Sil Lee, Hyo-bin Nam, Kwan Han Yoon
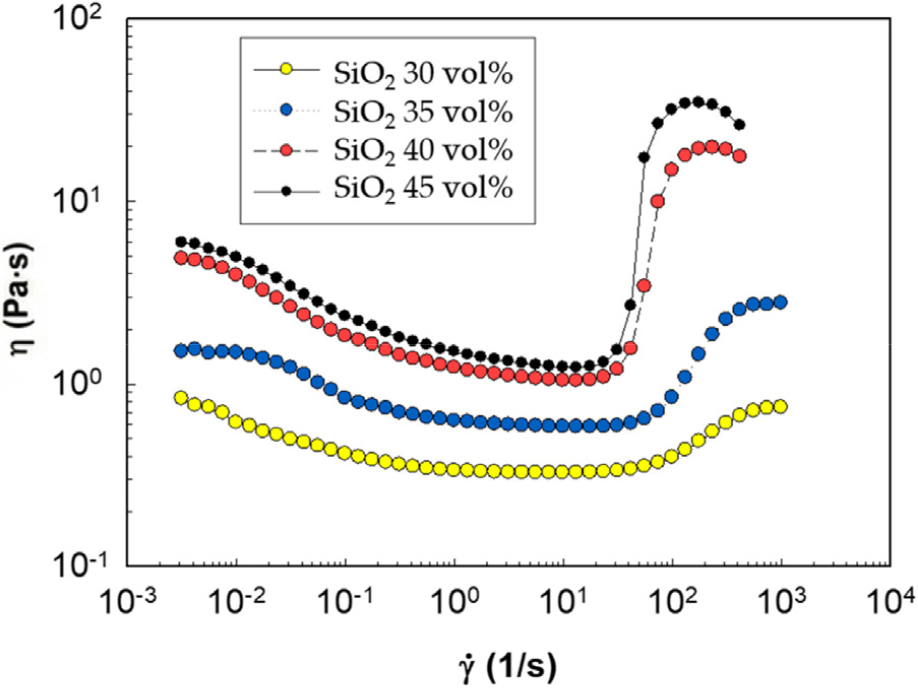
- This study investigates the rheological properties of shear thickening fluids (STFs) formulated by dispersing silica particles in polyethylene glycol (PEG), with the …
- This study investigates the rheological properties of shear thickening fluids (STFs) formulated by dispersing silica particles in polyethylene glycol (PEG), with the incorporation of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs). The influences of silica particle content, carbon nanotube (CNT) loading, and surface functionalization were systematically examined. Rotational rheometry demonstrated that CNT addition significantly reduced the critical shear rate while enhancing the maximum viscosity of the STF. Systematic analysis demonstrated that MWNT incorporation significantly reduces the critical shear rate and enhances the maximum viscosity of the STF by forming bridging networks that reinforce shear-induced hydro-clusters. Crucially, acid-functionalization was established as a viable technique to improve CNT dispersion and stability, allowing for higher loadings and stronger shear thickening responses necessary for designing lightweight, high-performance protective materials. Field emission scanning electron microscopy analysis provided microstructural evidence, confirming that the enhanced performance arises from the high-aspect-ratio CNTs forming a physical bridging network between the silica particles, which effectively stabilizes and reinforces the shear-induced hydro-clusters. These findings offer crucial design guidelines by defining the optimal concentration window and necessity of surface functionalization to maximize the high-performance potential of lightweight CNT-modified shear thickening fluids. Excessive CNT loading, however, induced agglomeration, leading to a deterioration of shear thickening. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Paper
- Carbonate-Suppressed Hydrothermal Synthesis of Tetragonal BaTiO3 Nanoparticles
- Woo Jun Sung, Tae Yeong Song, Do-Kyun Kwon
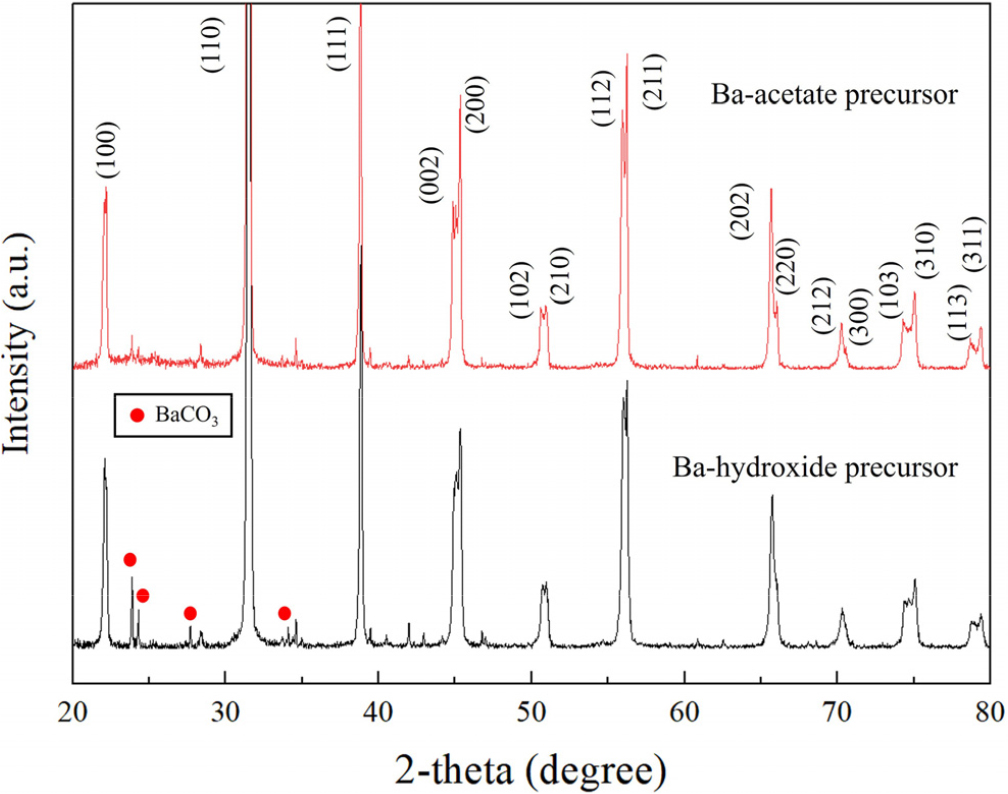
- We demonstrate a carbonate-suppressed hydrothermal route for synthesizing tetragonal BaTiO3 (BT) nanoparticles using barium acetate as the Ba source. Commercial TiO …
- We demonstrate a carbonate-suppressed hydrothermal route for synthesizing tetragonal BaTiO3 (BT) nanoparticles using barium acetate as the Ba source. Commercial TiO2 (P25) was converted to BT in KOH at 240 °C for 6 h without post-annealing. Relative to conventional Ba(OH)2 routes, the acetate precursor markedly reduced BaCO3 formation and narrowed the particle-size distribution. Systematic tuning of the Ba/Ti ratio (≥ 1.3) further optimized nucleation and growth, yielding uniform ~100 nm particles at Ba/Ti = 1.7 with the highest tetragonality (c/a ≈ 1.0076), as verified by XRD (002/200 splitting) and corroborated by Raman signatures of the tetragonal phase. Trace carbonate, when present, could be removed by mild weak-acid washing (e.g., acetic or citric acid) as effectively as with strong acids, but with improved process safety and practicality. The combined use of barium acetate, controlled Ba/Ti chemistry, and gentle carbonate removal yields phase-pure, highly tetragonal BT nanoparticles from low-cost precursors in a short dwell time, offering a scalable pathway to MLCC-grade powders. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Paper
- Plasma Resistant Highly Densified Yttria Ceramics Prepared via Dehydration Treatment of Raw Powders
- Jae-Hyeon Cho, Jin-Sam Choi
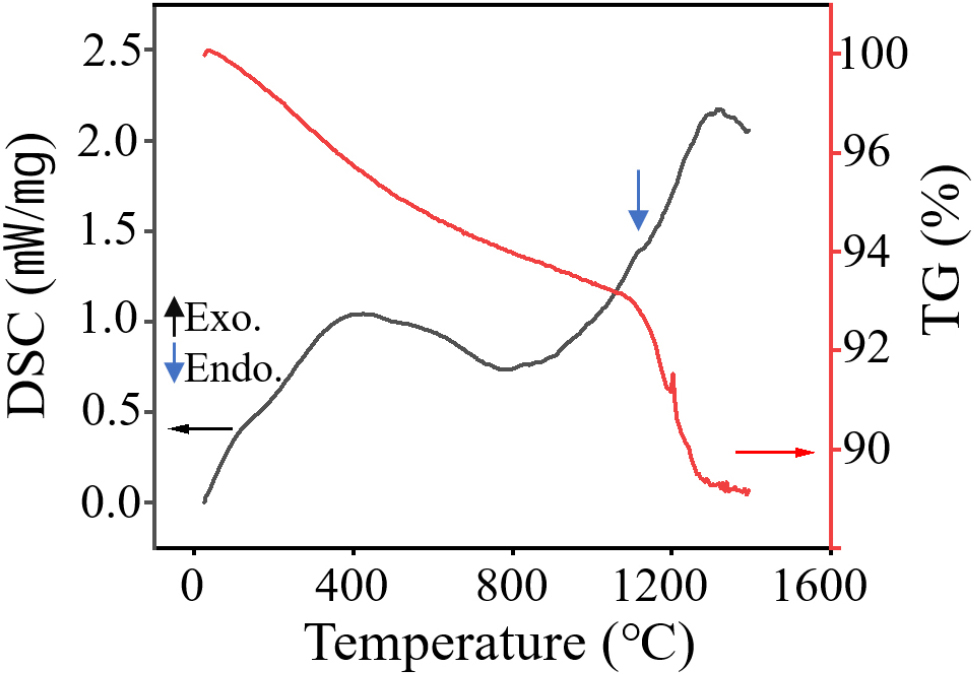
- This study identifies the crystalline defects commonly observed in conventional yttria ceramics, and proposes a processing route to produce highly densified yttria …
- This study identifies the crystalline defects commonly observed in conventional yttria ceramics, and proposes a processing route to produce highly densified yttria without the use of sintering aids. The primary objective is to obtain a dense yttria monolith with optimized microstructure and enhanced functional properties. The sintering behavior, mechanical performance, and plasma etching resistance of the yttria specimens were systematically analyzed as a function of the initial powder characteristics. A three-step sintering protocol was employed to suppress abnormal grain growth, yielding fully densified ceramics with uniform and controlled grain size distribution. Calcination of the yttria powder at 1,250 °C for 48 h effectively eliminated oxygen deficiencies and minimized hydration effects. The duration and temperature of each sintering stage significantly influenced grain evolution, which was reflected in the variations in Vickers hardness, Young’s modulus, and fracture toughness (KIC). The resulting yttria ceramics exhibited superior plasma resistance compared with Al2O3, ZrO2, quartz, and Si wafer, demonstrating markedly reduced weight loss during plasma etching. These findings highlight the critical role of proper initial powder treatment and precisely controlled sintering kinetics for achieving yttria monoliths with enhanced densification, mechanical integrity, and plasma erosion resistance. This work provides a practical route for high performance yttria ceramics, offering enhanced densification, structural stability, and the reliability necessary for integration into advanced systems exposed to harsh plasma environments. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Paper
-
Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AA1050/AA6061 Layered Sheets Processed by Cold Roll-Bonding and Subsequently Annealed
냉간압연접합 후 어닐링된 AA1050/AA6061 층상판재의 미세조직 및 기계적 특성
-
Hyeon-Jun Heo, Hyo-Sang Yoo, Hyunkyoo Cho, Seong-Hee Lee
허현준, 유효상, 조현규, 이성희
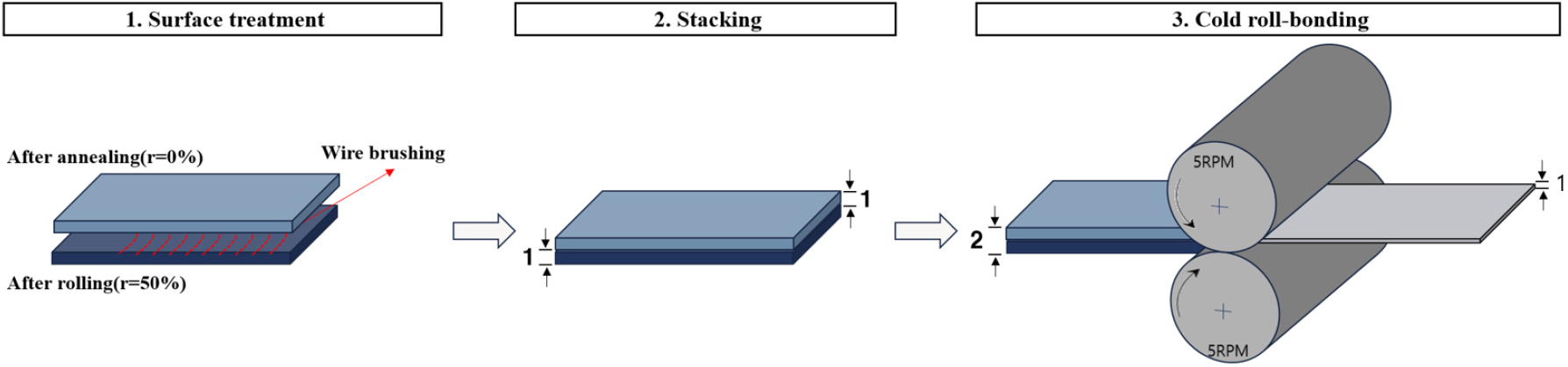
- A cold roll-bonding process using AA1050 and AA6061 sheets, in which the initial strain of AA1050 is higher than that of AA6061, …
- A cold roll-bonding process using AA1050 and AA6061 sheets, in which the initial strain of AA1050 is higher than that of AA6061, was employed to fabricate an AA1050/AA6061 layered sheet. The sheet was then annealed at various temperatures ranging from 200 to 400 °C. The as-roll-bonded sheet exhibited a typical deformation structure in which the grains were elongated along the rolling direction. The evolution of the microstructure in the layered sheets varied significantly depending on the location, resulting in an inhomogeneous distribution of hardness along the thickness direction. After annealing up to 300 °C, both the AA1050 and AA6061 regions still mainly exhibited a deformed structure. Complete recrystallization occurred in the specimens annealed at temperatures above 350 °C. The hardness decreased with increasing annealing temperature in both AA1050 and AA6061, but the decrease was greater in the AA6061 region than in the AA1050 region. Resultantly, at 350 °C or higher, hardness was almost the same in all regions. The specimen annealed at 350 °C exhibited the best mechanical properties in terms of the balance between tensile strength and elongation. It is concluded that AA1050/AA6061 layered Al sheets with excellent mechanical properties can also be fabricated by CRB when AA1050 has a higher initial strain than AA6061, and subsequent annealing. - COLLAPSE
-
Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AA1050/AA6061 Layered Sheets Processed by Cold Roll-Bonding and Subsequently Annealed
-
Research Paper
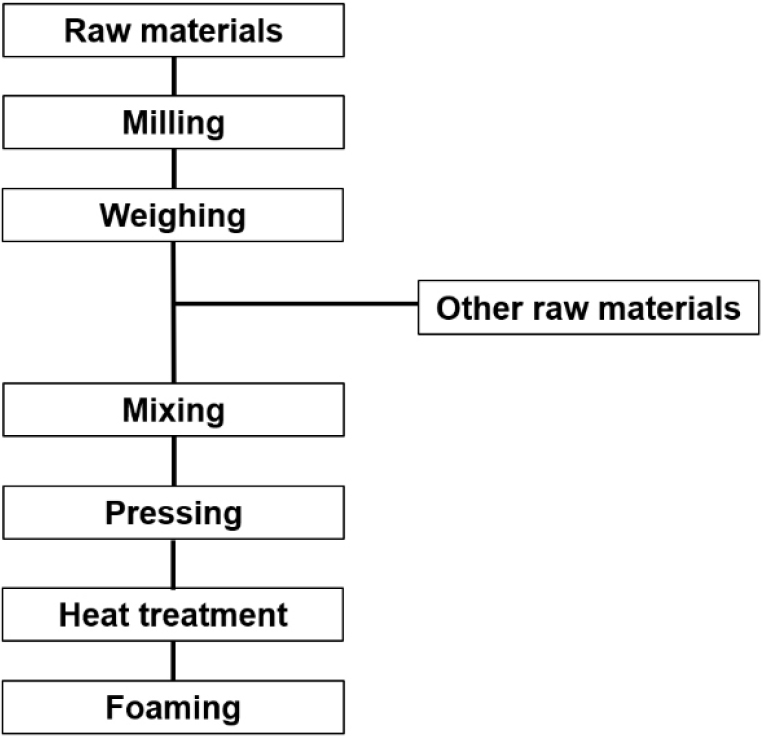
-
Fabrication of Foamed Glass and Its Properties Using Recycled Blast Furnace Slag
고로 슬래그 재활용 원료를 이용한 발포유리 제조 및 그의 특성
-
Ju Eun Park, Soon-il Kwon, Seunguk Song, Jinho Kim, Ji-Sun Lee
박주은, 권순일, 송승욱, 김진호, 이지선
- In this study, foamed glass was fabricated by adjusting the final heat treatment temperature. The heat treatment temperatures ranged from 900 °C …
- In this study, foamed glass was fabricated by adjusting the final heat treatment temperature. The heat treatment temperatures ranged from 900 °C to 1,100 °C at 50 °C intervals. Blast furnace slag (BFS) powder was mixed with foaming agent such as CaCO3, Ca3(PO4)2, Na2SiO3 and NaOH, pressed under compression, then heat treated to form a porous and stable glass structure. Their optical, thermal, and physical properties, including thermal coefficient, density, glass transition temperature (Tg) and X-ray diffraction patterns, were investigated. As the heat treatment temperature increased, the apparent density decreased from 1.44 g/cm3 to 1.03 g/cm3 while the porosity increased from 46.03 % to 58.89 %. Thermal coefficient decreased from 9.997 × 10-6 /K to 9.417 × 10-6 /K. The main XRD peak gradually shifted toward a lower angle, indicating an expansion of the glass network structure. Results showed that foamed glass based on BFS, developed with a porous structure, can be used as an effective thermal insulation material, suggesting the potential for the commercial utilization of slag. - COLLAPSE
-
Fabrication of Foamed Glass and Its Properties Using Recycled Blast Furnace Slag
-
Research Paper
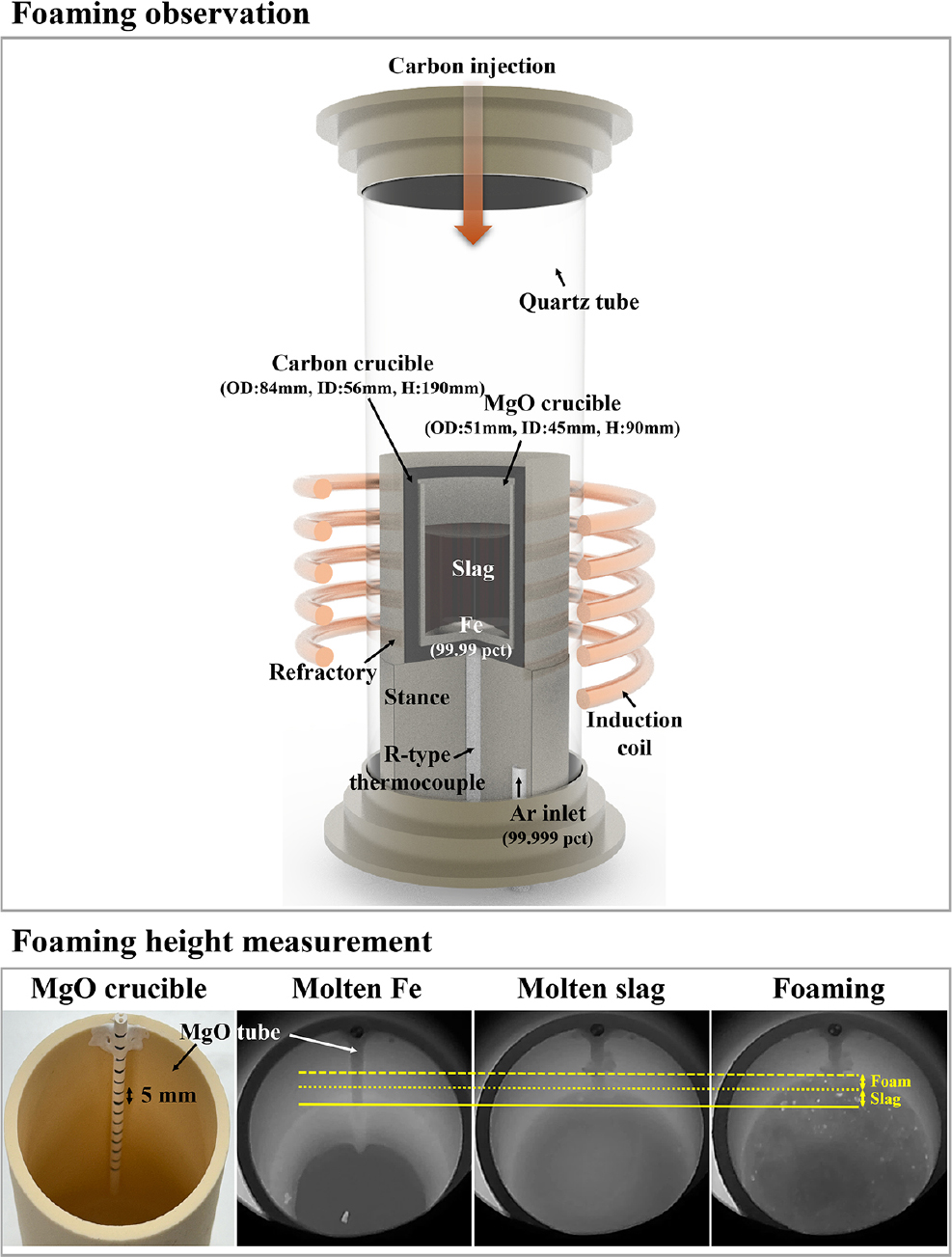
-
Enhancement of Slag Foaming in Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking through Spent Tire Utilization and Basicity Control
폐타이어 활용과 염기도 제어를 통한 전기로 제강 슬래그 포밍 특성 최적화
-
Gihyun Kim, Donghyeok Lim, Heung-Ju Cha, Seungwook Lee
김기현, 임동혁, 차흥주, 이승욱
- Electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking is increasingly adopting sustainable carbon sources to improve slag foaming and reduce energy consumption. Among them, spent …
- Electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking is increasingly adopting sustainable carbon sources to improve slag foaming and reduce energy consumption. Among them, spent tire-derived carbon represents a viable alternative to coal, offering high volatile and carbon contents. However, its elevated sulfur level and modified slag chemistry can markedly affect foaming stability and desulfurization. This study elucidates the interactive effects of spent tire substitution (0-30 wt%) and slag basicity (CaO/SiO2 = 1.5-2.4) on foaming dynamics, bubble evolution, and sulfur behavior at 1,600 °C. Real-time imaging and quantitative analyses demonstrated that moderate substitution (10-20 wt%) enhanced initial foaming due to volatile-induced gas release, whereas excessive addition (30 wt%) caused unstable coalescence and premature collapse from sulfur-driven surface tension reduction. Lower basicity limited early foaming but improved long-term stability via increased viscosity, while higher basicity promoted rapid collapse and reduced sulfur retention. The optimal condition (CaO/SiO2 = 2.0) maintained stable foaming for over 40 min, achieving superior sulfur capture (about 24 %) and minimal refractory attack. Overall, these findings reveal the mechanistic coupling between carbon source, basicity, and interfacial properties, offering practical guidance for sustainable slag design and efficient sulfur control in EAF operations employing waste-derived carbonaceous materials. - COLLAPSE
-
Enhancement of Slag Foaming in Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking through Spent Tire Utilization and Basicity Control
-
Research Paper
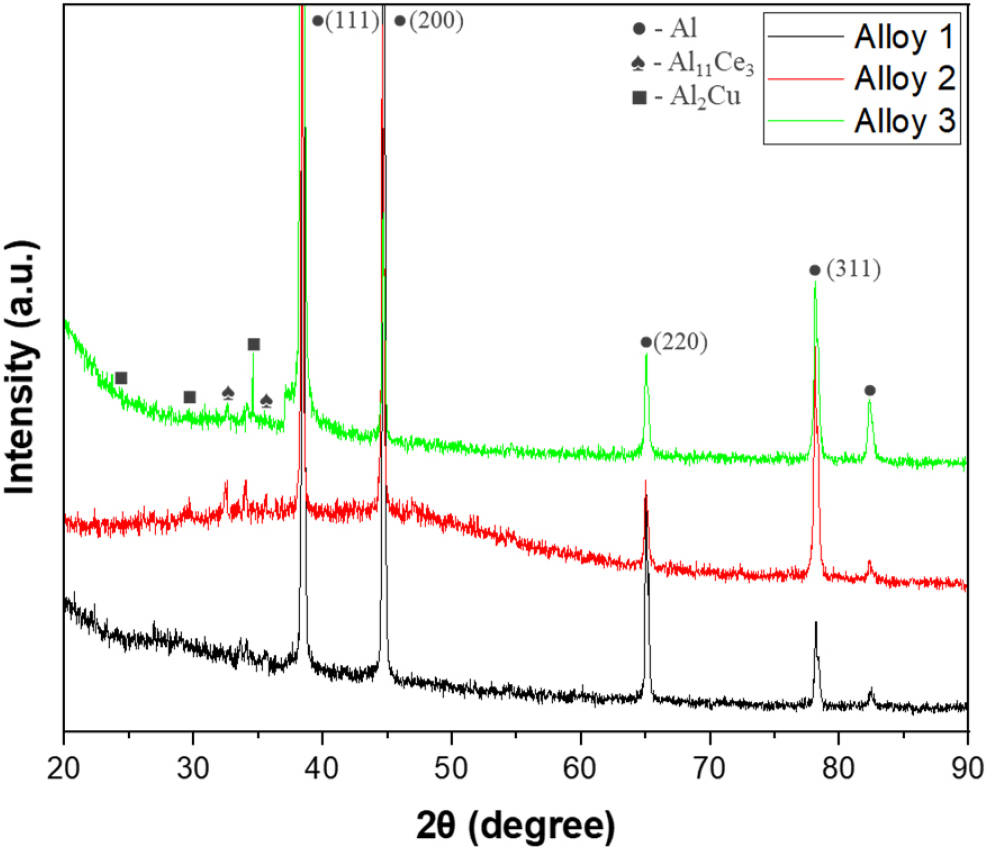
-
Effect of Cu Addition on Phase Formation, Recrystallization, and Mechanical Properties of Al-Zn-MM-Mg Alloys
Cu 첨가에 따른 Al-Zn-MM-Mg계 합금의 상 형성, 재결정 및 기계적 특성 변화
-
Byeong-Kwon Lee, Eun-chan Ko, Yong-Ho Kim, Hyo-Sang Yoo, Kyu-Seok Lee, Sung-Ho Lee, Hyeon-Taek Son, Tae-Hoon Kim
이병권, 고은찬, 김용호, 유효상, 이규석, 이성호, 손현택, 김태훈
- In this study, Cu was added in amounts of 0, 0.5, and 1 wt% to Al-1Zn-0.5MM-0.3Mg alloys to investigate its effects on …
- In this study, Cu was added in amounts of 0, 0.5, and 1 wt% to Al-1Zn-0.5MM-0.3Mg alloys to investigate its effects on phase formation, microstructural evolution, recrystallization behavior, and mechanical properties under as-cast and extruded conditions. Additional Al2Cu phases appeared with increasing Cu addition. EBSD (electron backscatter diffraction) analysis of the extruded alloys revealed that the average grain size boundaries [HAGB (high angle grain boundary), > 15°] increased from 0.124 to 0.299, confirming recrystallization was significantly enhanced by the addition of 1 wt% Cu. Furthermore, the maximum ODF(orientation distribution function) intensity decreased from 6.597 to 3.88 (M.R.D.), indicating that the crystallographic texture became more randomized as recrystallization progressed. Tensile testing showed that the yield strength (YS) and ultimate tensile strength (UTS) increased from 56.28 to 62.28 MPa and from 91.58 to 152.73 MPa, respectively, due to grain refinement and both solid-solution and precipitation strengthening by Cu. These findings demonstrate that adding Cu effectively controls phase formation, recrystallization, and mechanical properties in Al-Zn-MM-Mg alloys. - COLLAPSE
-
Effect of Cu Addition on Phase Formation, Recrystallization, and Mechanical Properties of Al-Zn-MM-Mg Alloys
-
Research Paper
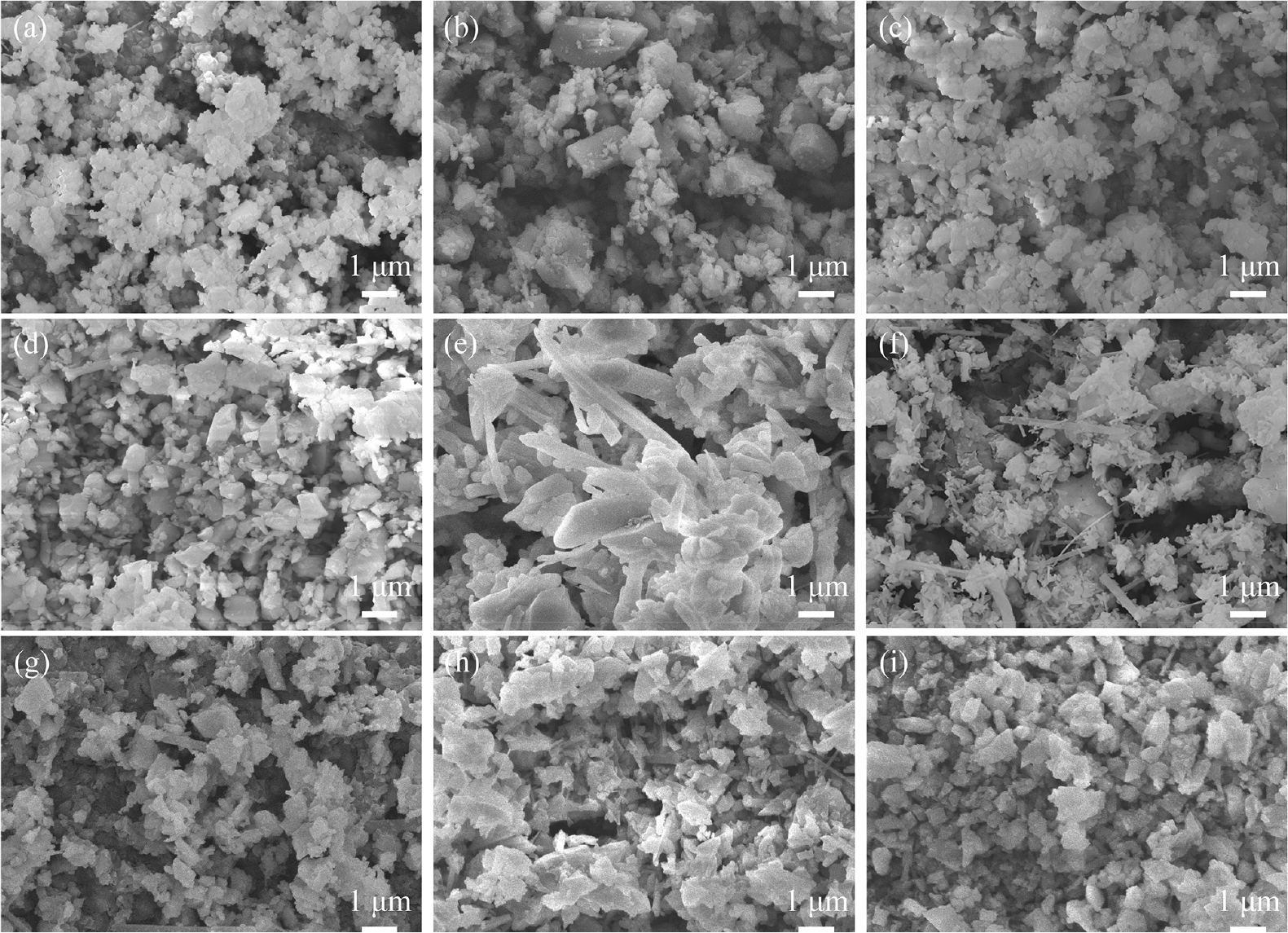
-
Correlation between the Properties of Commercial Silicon Nitride Powders and their Densification Behavior
질화규소 상용분말의 특성과 치밀화 거동의 상관관계
-
Cheng-Cai Zhao, Mi-Ju Kim, Ha-Neul Kim, Young-Jo Park, Jae-Woong Ko, Jae-Wook Lee
Cheng-Cai Zhao, 김미주, 김하늘, 박영조, 고재웅, 이재욱
- The quality of various commercial silicon nitride raw powders was compared and evaluated. Various powder characteristics and sinterability of low-cost Chinese powders …
- The quality of various commercial silicon nitride raw powders was compared and evaluated. Various powder characteristics and sinterability of low-cost Chinese powders were compared with those of powders from advanced manufacturers. Powder characteristics such as particle size, agglomeration, impurity content, and β phase fraction, as well as bulk characteristics such as β phase fraction and sintered density were investigated. The Chinese powder showed characteristics that were inferior to the E10 powder from UBE, Japan in most evaluated characteristics, but were comparable to the powders from other advanced manufacturers. However, at high temperature sintering of 1,800 °C, the sintered density of the Chinese powder was noticeably lower than that of the other powders. The correlation between various powder characteristics and sintered density was also quantified using the Pearson correlation coefficient. In the 1,700 °C sintered specimens, the particle size and β phase fraction were found to have a strong negative correlation with the sintered density. In contrast, the 1,800 °C specimens did not show any powder properties with a strong correlation to the sintered density. - COLLAPSE
-
Correlation between the Properties of Commercial Silicon Nitride Powders and their Densification Behavior
-
Research Paper
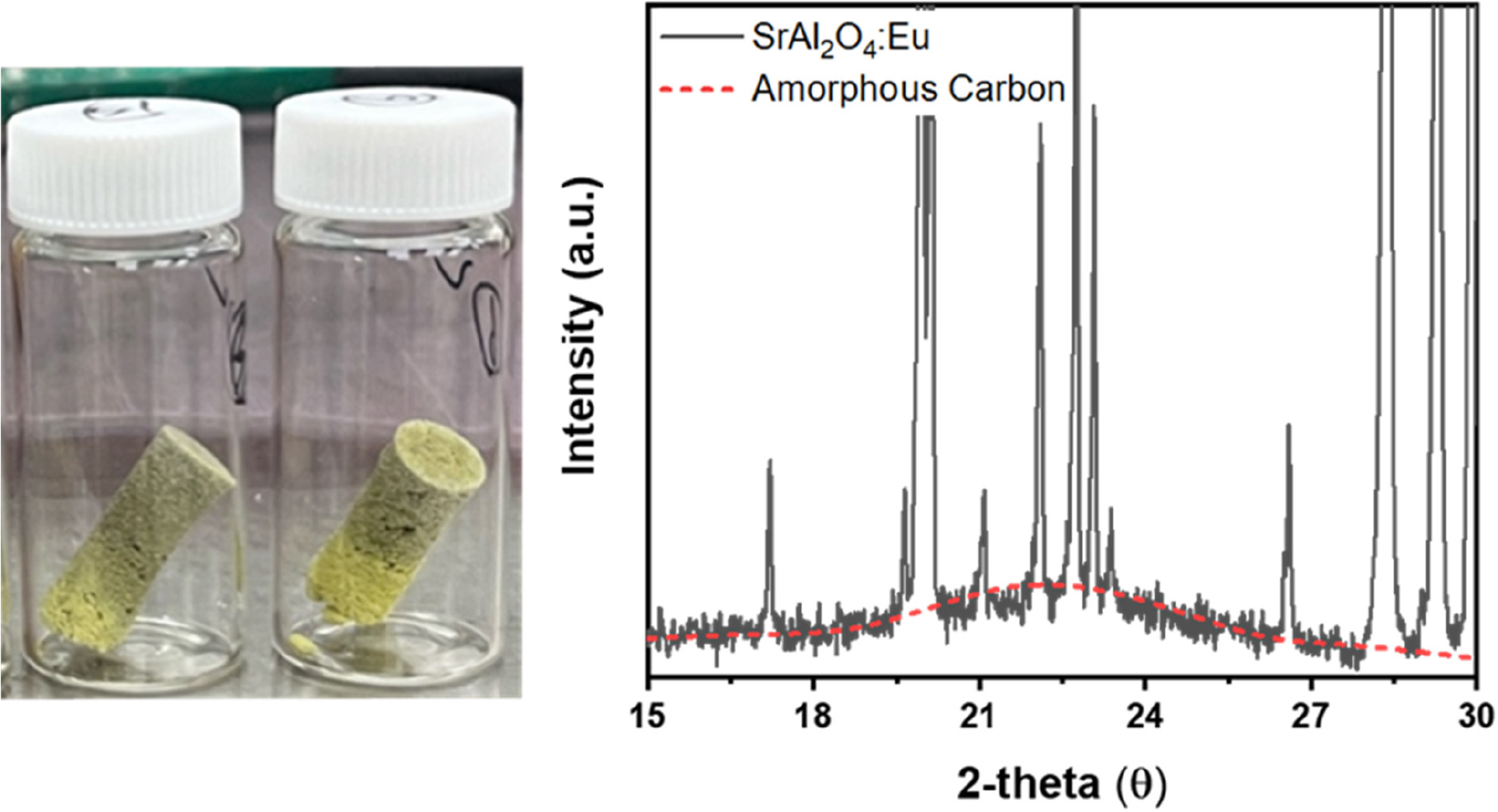
-
Enhancement of Luminescence Efficiency of SrAl2O4:Eu Phosphors via Dispersion-Induced Decarburization Process
분산 기반 탈탄 공정 도입을 통한 SrAl2O4:Eu 형광체의 발광 효율 향상
-
Chaeyoun Kim, Youngseung Choi, Seongju Park, Seoyeon Park, Sung-jin Yang, Ji-seong Go, Byungha Shin
김채연, 최영승, 박성주, 박서연, 양성진, 고지성, 신병하
- This study proposes a Dispersion-Induced Decarburization (DID) process using polar solvents to address the degradation of luminescence efficiency in SrAl2O …
- This study proposes a Dispersion-Induced Decarburization (DID) process using polar solvents to address the degradation of luminescence efficiency in SrAl2O4:Eu phosphors caused by carbon contamination from carbon crucibles during high-temperature synthesis. Conventional high-temperature oxidation treatments are effective for carbon removal but induce the oxidation of Eu2+ ions and structural collapse of the SrAl2O4 host, resulting in severe degradation of luminescence properties. The proposed DID process physically removes carbon impurities by dispersing SrAl2O4:Eu powders in highly polar solvents such as distilled water (DI), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP), and N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF). Among them, DI exhibited the highest purification efficiency, completely eliminating carbon-related diffraction peaks. As a result, the photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) of SrAl2O4:Eu improved from 32 % to 50 %, and a maximum PLQY of 55.2 % with a luminance of 6,000 cd・m-2 was achieved for the 20 mol% Eu-doped powder. This work presents a novel and effective purification strategy that overcomes carbon contamination in SrAl2O4:Eu phosphors, significantly enhancing their luminescence efficiency without structural damage. - COLLAPSE
-
Enhancement of Luminescence Efficiency of SrAl2O4:Eu Phosphors via Dispersion-Induced Decarburization Process
-
Special Issue KIMS - Review
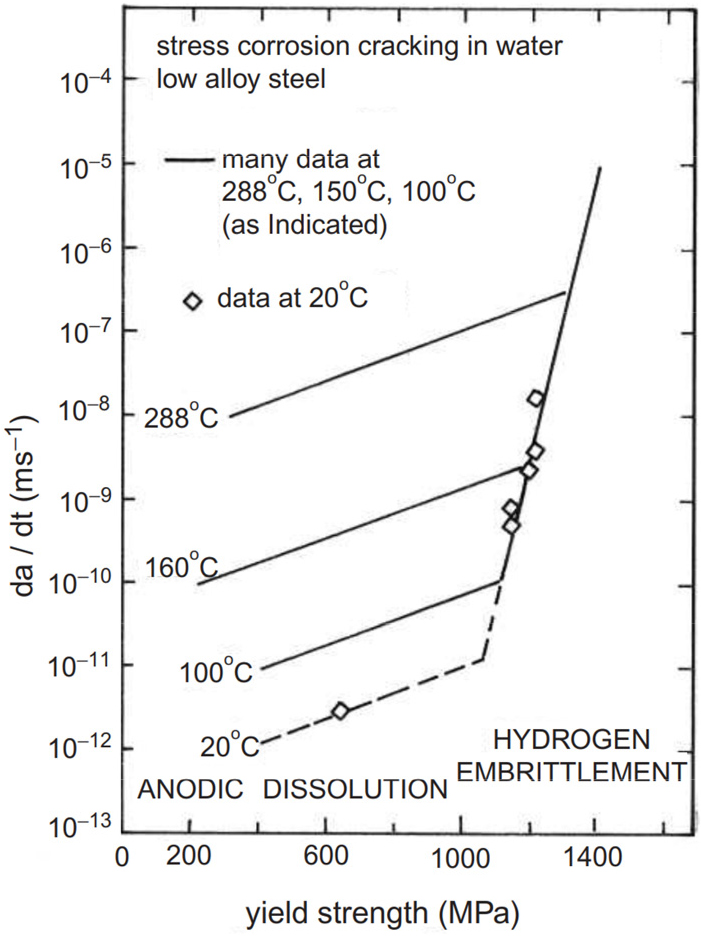
-
Recent Progress in Hydrogen Embrittlement Behavior Analysis of Steels using Cryogenic Atom Probe Tomography
Cryogenic Atom Probe Tomography 기반 철강소재 수소취성 거동 분석 기술 동향
-
Jisung Yoo, Jeong-Min Lee, Chang-Hoon Lee
유지성, 이정민, 이창훈
- Hydrogen embrittlement (HE) remains one of the most critical challenges in ensuring the structural integrity of steels for hydrogen energy infrastructures, including …
- Hydrogen embrittlement (HE) remains one of the most critical challenges in ensuring the structural integrity of steels for hydrogen energy infrastructures, including storage and transport systems. Despite decades of research, the underlying mechanism of HE is still not fully understood due to the complexity of hydrogen-microstructure interactions across multiple length scales. Cryogenic Atom Probe Tomography (Cryo-APT) has recently emerged as a unique method of providing near-atomic resolution and compositional sensitivity for hydrogen analysis, thereby enabling direct visualization of hydrogen distribution at defects, interfaces, and precipitates. This review summarizes recent progress in Cryo-APT-based investigations of hydrogen behavior in steels, with a focus on trapping mechanisms, the role of microstructural features, and the synergistic activation of multiple HE mechanisms. Key technical developments, such as cryogenic workflows and isotope tracing, have significantly advanced the reliability of Cryo-APT hydrogen quantification. Case studies on ferritic-martensitic steels, pearlitic steels, and advanced high-strength steels highlight the potential of Cryo-APT to reveal both diffusible and non-diffusible hydrogen trapping. While current limitations include local sampling bias, experimental complexity, and signal interpretation challenges, continuous improvements in methodology and integration with multiscale modeling are expected to establish Cryo-APT as a core approach for elucidating HE mechanisms. This review provides a comprehensive perspective on the current technical state and future directions of Cryo-APT in HE researches. - COLLAPSE
-
Recent Progress in Hydrogen Embrittlement Behavior Analysis of Steels using Cryogenic Atom Probe Tomography
-
Special Issue KIMS - Review
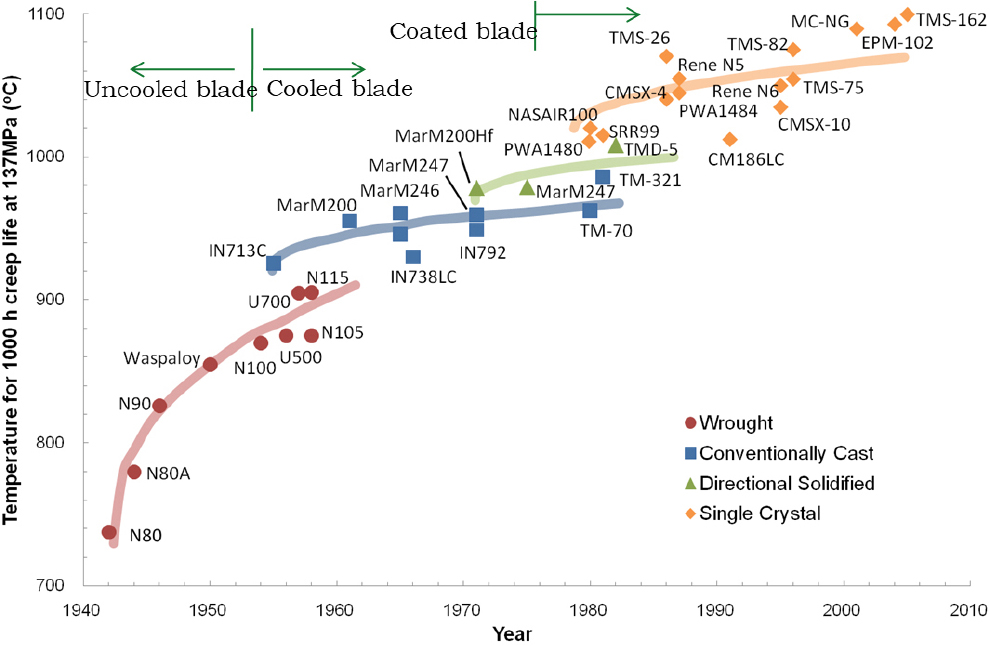
-
Development Trends of Single-Crystal Superalloys for Gas Turbines and the Current Status of Domestic Re-Free Alloy Development
가스터빈용 단결정 초내열합금 개발 동향과 국산 Re-free 단결정 초내열합금 개발 현황
-
Jeonghyeon Do, Sangwon Lee, Joong Eun Jung, In Soo Kim, Baig-Gyu Choi
도정현, 이상원, 정중은, 김인수, 최백규
- As science and technology advance, the demand for materials capable of withstanding extreme environments has steadily been increasing. Among them, structural materials …
- As science and technology advance, the demand for materials capable of withstanding extreme environments has steadily been increasing. Among them, structural materials that can operate reliably at high temperatures remain a critical field of development. Single-crystal nickel-based superalloys are among the most advanced metallic materials, capable of sustaining stresses at the highest operating temperatures, and are widely used for gas turbine blades. Since the efficiency of a gas turbine increases with higher turbine inlet temperature, the development of alloys capable of operating under such extreme conditions has been a continuing challenge. Significant progress has been achieved by adding refractory elements such as Re and Ru, leading to superalloy generations classified according to their content. While advanced countries initially led the development of 4th and 5th generation alloys containing high amounts of Re and Ru, recent trends have emphasized cost competitiveness, by reducing these expensive elements while maintaining high-temperature performance. Alongside Western countries, China has also invested heavily in optimizing Re and Ru content for material self-reliance. For Korea, the local realization of single-crystal superalloys is essential not only for industrial gas turbines but also for defense-related jet engines. At the Korea Institute of Materials Science, extensive research has been carried out to develop alloys tailored to different conditions. Recently, a Re-free single-crystal superalloy was developed that exhibits superior creep resistance compared to conventional Re-containing alloys, even outperforming TMS-1700, the world-class Re-free alloy developed at NIMS, Japan. Optimization studies toward commercialization are ongoing, contributing to the national goal of self-reliance in extreme high-temperature materials. - COLLAPSE
-
Development Trends of Single-Crystal Superalloys for Gas Turbines and the Current Status of Domestic Re-Free Alloy Development
-
Special Issue KIMS - Research Paper
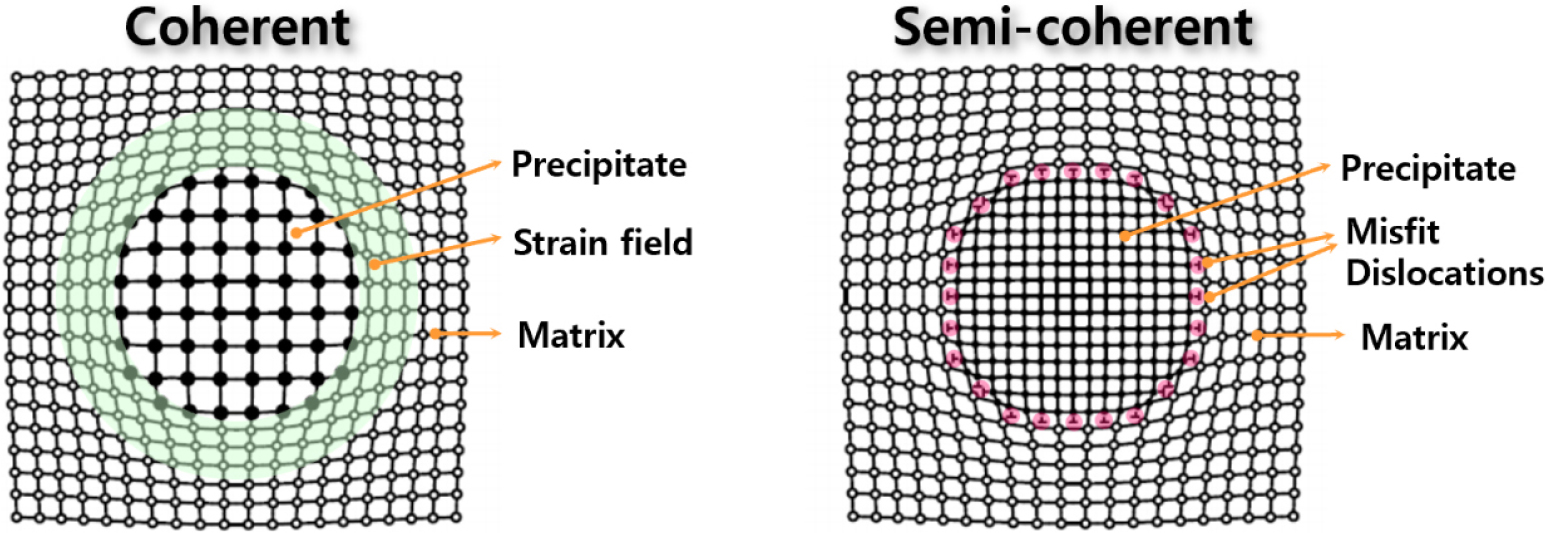
-
Design of a Ferritic Heat-Resistant Alloy with Improved Corrosion Resistance and Ductility
우수한 부식 저항성과 연성을 갖는 페라이트계 내열 합금 설계
-
Ka Ram Lim
임가람
- High-entropy alloys (HEA) have emerged as promising structural materials for use in extreme environments where conventional alloys face limitations. In this study, …
- High-entropy alloys (HEA) have emerged as promising structural materials for use in extreme environments where conventional alloys face limitations. In this study, ferritic Fe-Al-Cr-Ni-Ti alloys were developed by employing the HEA design concept to promote coherent L21 precipitation within a BCC matrix. The systematic variation of Al content enhanced lattice coherency, precipitation strengthening, and the rapid formation of protective Al2O3 scales. The alloy with 16 at% Al exhibited superior high-temperature mechanical performance, showing a yield strength of approximately 400 MPa and ~5 % uniform elongation at 700 °C, exceeding the use temperature limit of conventional steels. Steam oxidation tests demonstrated the formation of dense, continuous alumina films, while hot rolling and grain refinement effectively improved room-temperature ductility. These findings indicate that Fe-Al-Cr-Ni-Ti alloys offer a cost-effective pathway to achieve a balanced combination of heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and mechanical processability, suggesting their potential as strong candidates for next-generation energy and high-temperature structural applications. - COLLAPSE
-
Design of a Ferritic Heat-Resistant Alloy with Improved Corrosion Resistance and Ductility
-
Special Issue KIMS - Research Paper
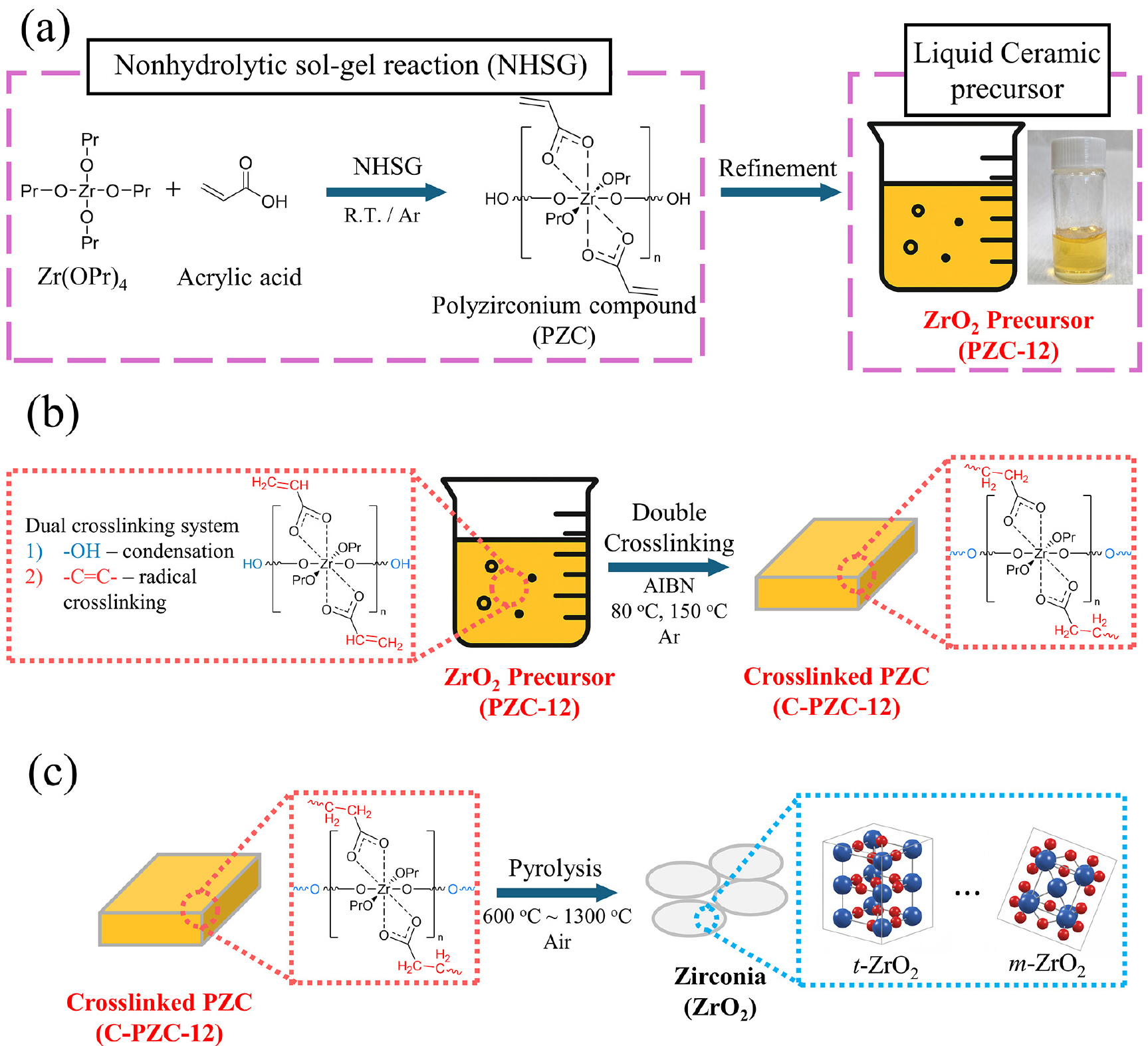
-
Dual Crosslinking-Based Synthesis of High-Performance Liquid Zirconia Precursors for Polymer Infiltration Pyrolysis Applications
이중가교법을 적용한 저점도, 고수율 지르코니아 액상전구체 합성
-
Jae-Il So, Keon-ho Lee, HoYoung Hwang, Jinkyu Choi, Sea-Hoon Lee
소재일, 이건호, 황호영, 최진규, 이세훈
- Ultra-high temperature ceramics (UHTCs) exhibit extremely high melting points (> 2,500 °C) and maintain structural stability under severe conditions. However, their intrinsic …
- Ultra-high temperature ceramics (UHTCs) exhibit extremely high melting points (> 2,500 °C) and maintain structural stability under severe conditions. However, their intrinsic brittleness and oxidation vulnerability limit their direct application in aerospace components exposed to extreme environments. To overcome these limitations, UHTC-based composites reinforced with secondary phases such as ZrO2 are required to improve fracture toughness and oxidation resistance. The polymer infiltration and pyrolysis (PIP) process provides a promising fabrication route for such composites, offering densification of porous matrices with liquid precursors while maintaining uniform microstructures. Here, we report a novel zirconia precursor (PZC-12) synthesized through a sol-gel reaction of zirconium propoxide with acrylic acid (1:2 molar ratio). The liquid precursor exhibited a suitable viscosity (~518 cP) and enabled dual crosslinking via hydroxyl condensation combined with radical polymerization of vinyl groups. Consequently, effective thermal curing was accomplished upon heating at 80 °C for 12 h. This strategy minimized premature decomposition and achieved a high ceramic yield of 52.7 %. Pyrolysis at 600 °C in air produced nanosized t-ZrO2, which transformed into m-ZrO2 with grain growth at higher temperatures. Applied in PIP, a ZrB2-ZrO2 composite was successfully fabricated, demonstrating that dual crosslinking is critical for high-yield, reliable PIP-based UHTC composites. - COLLAPSE
-
Dual Crosslinking-Based Synthesis of High-Performance Liquid Zirconia Precursors for Polymer Infiltration Pyrolysis Applications
-
Special Issue KIMS - Research Paper
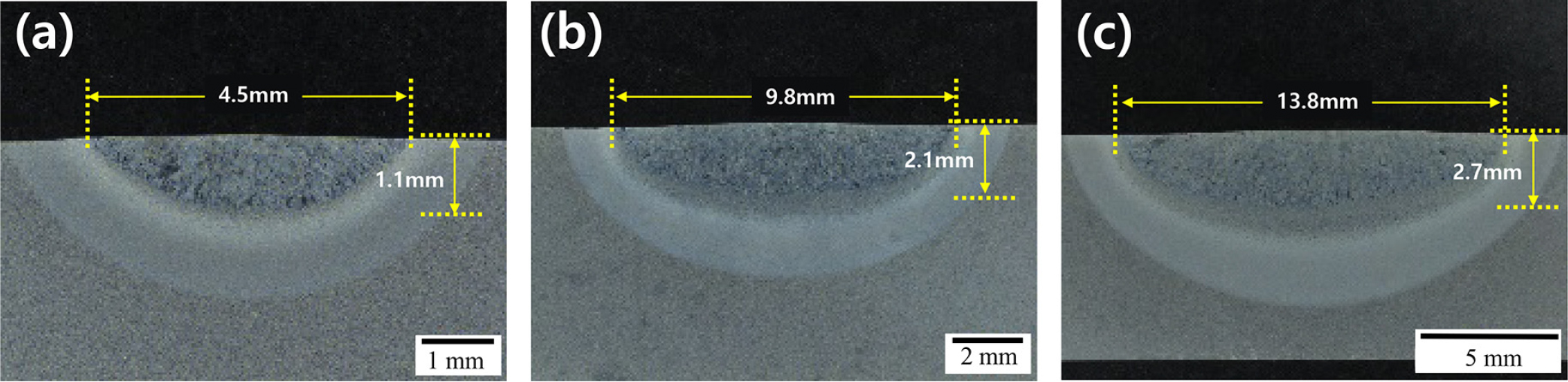
-
Effect of Heat Input on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Reduced Activation Ferritic/Martensitic Steel Weld Metal
핵융합로 구조용 저방사화강 용접금속의 미세조직 및 기계적 특성에 미치는 입열량의 영향
-
Kyoung-Hwan Kim, Gitae Park, Chan Kyu Kim, Chang-Young Oh, Sangwoo Song, Chang-Hoon Lee, Yongjoon Kang
김경환, 박기태, 김찬규, 오창영, 송상우, 이창훈, 강용준
- In this study, the effect of welding heat input on the microstructure and mechanical properties of reduced-activation ferritic/martensitic steel weld metal was …
- In this study, the effect of welding heat input on the microstructure and mechanical properties of reduced-activation ferritic/martensitic steel weld metal was investigated to provide a basis for developing welding technology for this steel, which is considered a structural material for fusion reactor blankets. Autogenous bead-on-plate gas tungsten arc welding was performed with heat inputs of 0.57, 1.38, and 2.32 kJ/mm, and the microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of the weld metal were analyzed. The fraction of residual δ-ferrite in the weld metal varied depending on the welding heat input, which acted as a primary factor contributing to the reduction in weld metal strength, although it remained higher than that of the base metal. In addition, the effect of post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) at 730 °C for 1 h was evaluated. Before PWHT, the weld metal exhibited significantly higher hardness compared with the base metal. However, after PWHT, its hardness was substantially reduced, thereby minimizing the differences in hardness of the weld and the base metal. - COLLAPSE
-
Effect of Heat Input on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Reduced Activation Ferritic/Martensitic Steel Weld Metal
Journal Informaiton
 Korean Journal of Materials Research
Korean Journal of Materials Research
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Korean Journal of Materials Research
Korean Journal of Materials Research











